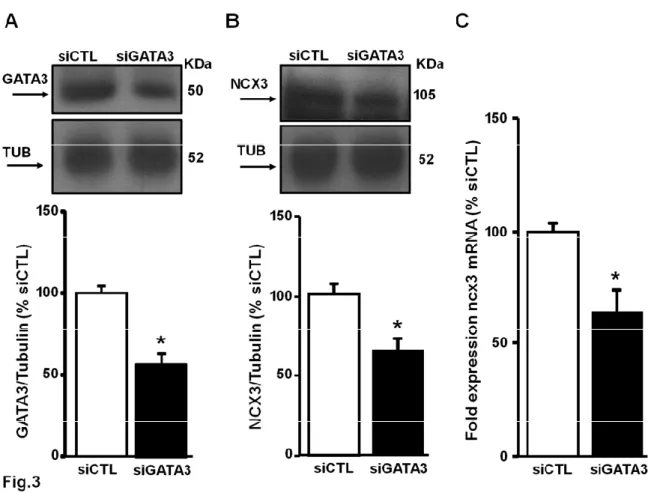
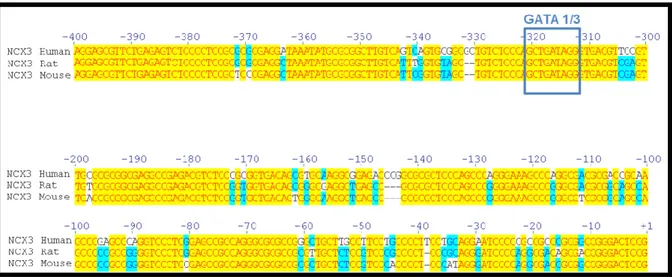
Identification of Epigenetic Mechanisms Regulating NCX3 in in Vivo Model of Brain Ischemic Preconditioning
Testo completo
Figura



Documenti correlati
Nelle prove di polarizzazione potenziostatica le miscele nitrito - benzoato (30% - 70%), nitrito - glutammina (30% - 70%) e miscela nitrito - DMEA (50% - 50%) aumentano in
Un complesso rapporto si instaura tra la nascente istituzione pubblica ed il notariato: questi tecnici del diritto hanno già una tradizione di auto- nomia
The possibility to assess the contribution of brain histamine (HA) to specific behavioral changes is a complex task, taking into consideration the broad modulatory
In Section 3, we introduce our basic representation of BoD constraints with layered preferences, and provide a general constraint propagation algorithm grounded on
Here, to make up for the relative sparseness of weather and hydrological data, or malfunctioning at the highest altitudes, we complemented ground data using series of remote sensing
Per ridare speranza ai giovani occorre quindi lavorare su più versanti: un versante or- ientativo, finalizzato alla definizione di un progetto professionale e/o for-
The Ophiolitic Nappe + Sub- ophiolitic Mélange overthrust discontinuous slices of Early Cretaceous continental margin sequences, mostly consisting of deep water carbonate,
The results of this study demonstrate that pen- tamidine, via direct inhibition of S100B protein, attenuates 1/reactive gliosis and neuroinflammation induced