15
3. MODULATION TECHNIQUES FOR PLC CHANNELS
The OFDM modulation technique has gained an increased interest during the last years . It has been adopted as a standard in the European digital audio broadcast (DAB) system . OFDM-based discrete multitone (DMT) systems are also examined
for broadband digital communication on the existing copper network. OFDM improves on FDM by making the sub-carriers that are adjacent to each
other orthogonal. Since the sub-carriers are orthogonal they are considered to be independent of each other and a guard band between each sub-carrier is not needed. This makes OFDM more frequency efficient than FDM. Some implementations of OFDM use some of the sub-carriers for error correction codes to make the transmission more reliable.
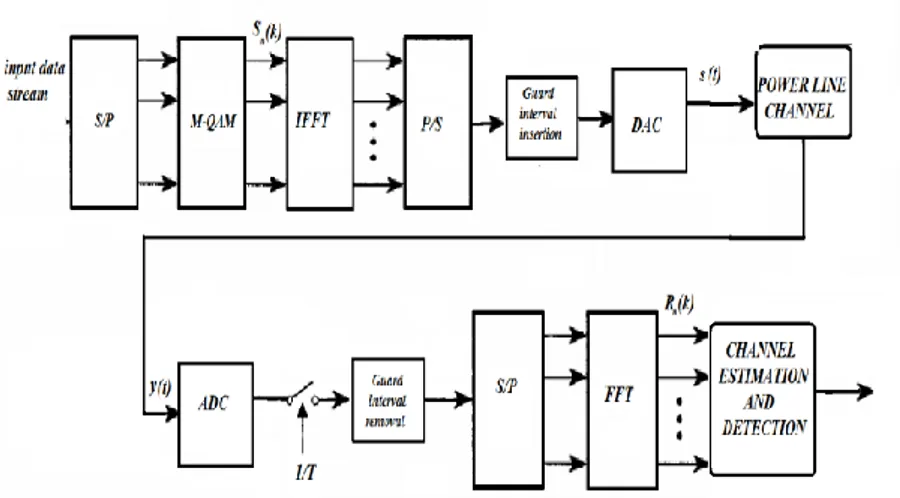
Consider a frame interval m , the transmission of a vector of N complex symbols
m k
X , k1...N, where N is the number of subcarrier, taken from some signal constellation (e.g., PSK, QAM, M-QAM) is illustrated Fig. 1. The data m
k
X are
modulated on N subcarriers by an inverse discrete Fourier transform IFFT, a vector of2N real valued channel symbols, m
n
I ,n1,..., 2N1 , the samples of the baseband OFDM signal. This data vector is serially transmitted over a discrete-time channel with envelope I t
given by:
1 0 1 2 1 _ 2 / 2 / 0 1 ( ) 1 2 N m n m n m N N m m jnk N jnk N k n k k k N s t I g t nt mNT and I I e I e N
_ m kI is the complex coniugate, Tis the discrete sampling time (NTis the OFDM frame duration), g t
is the pulse shaping filter adopted given by:2 2 2 cos ( ) sin 4 1 t t T g t K c t T T
16 The Power line channel acts as a time variant filter.
The signal at the receiver is the convolution of the transmitted signal i t
and the channel impulse response and a sum of additive noise produced by a mixture Gaussian and impulsive noise. In general the received signal is expressed by:m m m m k k k k
R H I W
Where m k
R is the received value at the kth sub channel, m k
H is the cannel
complex gain and k n
W is the complex gain.
OFDM splits the available bandwidth into many narrow band channels (typically 100-8000) and the number N of subcarrier is design in order that each sub channel will have a narrow bandwidth. The carriers for each channel are made orthogonal to one another, allowing them to be spaced very close together. Because of this there is no great need for users to be time multiplex as in TDMA, thus there is no overhead associated with switching between users.
The big questions to achieve minimal signal distortion are the strong fading characteristics of the channel, the loss of orthogonality caused by imperfect synchronization and by the cyclic short time-variations in the channels. For this reasons is necessary investigating a batter estimation and equalization method for OFDM transmission.
17 A problem in the design of OFDM receivers, and receivers for block transmission systems in general, is the unknown time instant to start sampling a new frame. Another problem in multi-carrier systems is the mismatch of the oscillators in the transmitter and receiver but we analyze the OFDM problem in the next section.
3.1 OFDM signals in nonlinear channel
The major drawback of the OFDM technique is its large signal dynamic caused by the high number of subcarriers with random phase and amplitude, which are summed in the modulator. The effects fading, synchronization, noise and interference may significantly compromise the quality of the received signal in the frequency band below 30 MHz.
When a multicarrier signal is amplified, the effects of distortions are:
1. Multicarrier transmission systems show a great sensitivity to the nonlinear distortion effects caused by the use of high power amplifiers (HPA) or clipping devices.
2. Intermodulation effects, which occur between the OFDM subchannels causing spectral spreading of the transmitted signal and adjacent subchannel interference.
3. Intermodulation will also cause adjacent-channel interference (ACI) if more than one OFDM signal is transmitted. In general, even if the source of nonlinearity is memoryless, the presence of filtering before it makes the overall transmission chain acting as a nonlinear system with memory. However, in this case, no intersymbol interference (ISI) between OFDM symbols is present due to the rectangular shape of the transmitted pulses.
For this reasons, a preliminary study of the system is required to find a good tradeoff between transmitted power and degradation caused by nonlinear distortions. In a multipath environment, a transmitted symbol takes different times to reach the receiver through different propagation paths. From the receivers point of view, the channel introduces time dispersion in which the
18 duration of the received symbol is stretched. Extending the symbol duration causes the current received symbol to overlap previous received symbols and results in intersymbol interference (ISI) .
In OFDM, ISI usually refers to interference of an OFDM symbol by previous OFDM symbols. In OFDM, the spectra of subcarriers overlap but remain orthogonal to each other. This means that at the maximum of each subcarrier spectrum, all the spectra of other subcarriers are zero. The receiver samples data symbols on individual subcarriers at the maximum points and demodulates them free from any interference from the other subcarriers. Interference caused by data symbols on adjacent subcarriers is referred to inter carrier interference (ICI).
OFDM signals can be treated as a series of independent and identically distributed modulated carriers.
The high peak-to-average power ratio of an OFDM signal makes it susceptible to nonlinear or clipping distortions, as the signal peaks may occasionally thrust into the saturation region of the power amplifier. The result is BER degradation and adjacent channel interference. Moreover, this nonlinear effect will depend on the multilevel modulation applied and will be greater than the single carrier equivalent system. In the presence of both nonlinear distortion and additive Gaussian noise, optimized output power back-off is needed to reduce the OFDM signal degradation.