Introduction to
Experimental section
31
Introduction to experimental section.
One of the main negative regulator of p53 is the ubiquitin E3 ligase Murine Double Minute 2 protein, MDM2, which is able to interact with p53 and mediate its degradation by protoesoma, thus blocking its activity. MDM2 downregulates p53 transcription factor activity by binding to its transactivation domain (TAD). As many kinds of tumors show an inactivation of p53 pathway, nongenotoxic therapeutic strategies that activate p53 in one way or another are highly desirable. The inactivation of p53 pathway may depends on nucleotide mutation of TP53 gene (p53 mutated) or altered regulation of its function (p53 non mutated). When p53 is mutated, a valid strategy to promote mitochondria-mediated apoptosis seems to be the activation of the apoptotic factors Bax and Bak. On the contrar , when p53 is not mutated, but its altered functionality is related to the overexpression of MDM2 protein, the destruction of the p53-MDM2 interaction may represent a valuable strategy for the therapeutic treatment of cancer 7.
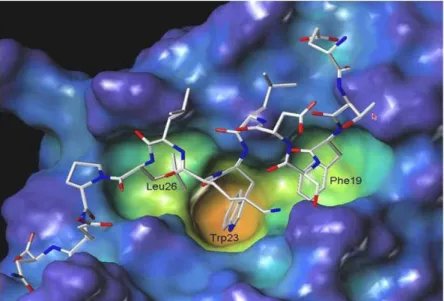
The MDM2-p53 complex is characterized by an MDM2 hot spot occupied by the critical p53 residues Phe19, Trp23 and Leu26, which are inserted into a deep hydrophobic pocket on the surface of MDM2. The hydrophobic contacts are augmented by two hydrogen bonds, one between the Phe19 backbone amide NH of p53 and the carbonyl of the Glu72 side chain of MDM2 at one end of the cleft, and another between the p53 Trp23 indole NH and the MDM2 Leu54 backbone carbonyl group inside the cleft25 (Figure 20).
32
Historically, it has been difficult to develop small-molecule inhibitors of non-enzyme protein-protein interaction, but the existence of such a well-defined pocket on the MDM2 surface raised the expectation that compound with low molecular weight could be found that would block the interaction of MDM2 with p53 31.
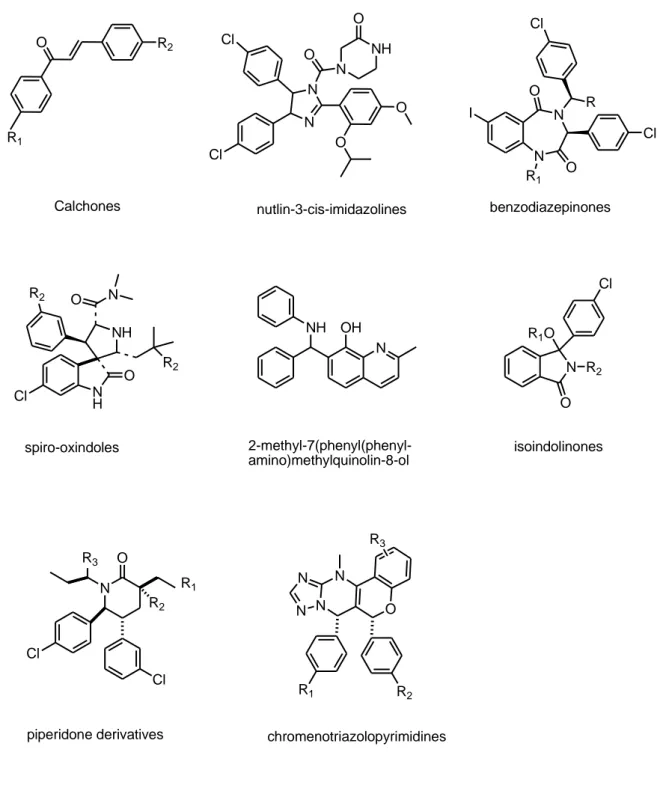
Structural data suggest that a synthetic molecule featuring three hydrophobic groups in an orientation that mimics the side chain of the three key amino acids of p53 should occupy the MDM2 cleft and inhibit the p53-MDM2 interaction. The first reported potent and selective small molecule MDM2 antagonists were a class of cis-imidazolines, the nutlins (Figure 21). Crystal structure studies demonstrated that the nutlins bind to the p53 pocket of MDM2 mimicking the molecular interactions between MDM2 and the crucial amino acid residues from p53. Other small molecules have been developed including calchone-based inhibitors, benzodiazepinones, spiro-oxindoles, isoindolinones, piperidone derivatives, imidazolines and chromenotriazolpyrimidines (Figure 21).
Most of these small molecules share the common features of a rigid heterocyclic scaffold, decorated with p-halophenyl groups projected toward the phenylalanine and tryptophan binding pockets on the MDM2 surface.
33 R1 O R2 Calchones Cl N N N O NH Cl O O O nutlin-3-cis-imidazolines I N N O O Cl R Cl benzodiazepinones Cl R1 N H O NH R2 N O R2 spiro-oxindoles N OH NH 2-methyl-7(phenyl(phenyl-amino)methylquinolin-8-ol N O R2 R1O Cl isoindolinones piperidone derivatives N O R2 R1 R3 Cl Cl N N N N O R1 R2 chromenotriazolopyrimidines R3
34
Recently, we have designed and synthesized a new molecule the N-(2-phenylindol-3-yl-glyoxylyl)-Leucinephenylalanine ethyl ester I, that could mimic the p53 residues critical for the interaction with MDM2.
N H O O HN O HN O O I
Compound I was evaluated for the ability to activate p53-function in U87MG cell, a commonly used and thus well-studied glioblastoma cell line derived from a human grade IV glioma. The preliminary data showed that compound I was able to activate p53 gene transactivation function and to exert antitumor in vitro effects by activation of apoptotic process. These effects were time and dose-dependent suggesting, their specificity.
Molecular modelling calculations were performed to razionalized the biological activity of compound I. Figure 22 showed that this compound is able to interact with all the three lipophilic pockets and is also capable to occupy a fourth adiacent site with the latheral chain of Phenylalanine. This further interaction may accont for its high biological activity.
35
Figure 22. Molecular Modeling of the compound I
These data represented the rational for the investigation of a series of new derivatives from this class. In particular, we have designed and synthesized a small library of 2-phenylindol-3-glyoxylyl derivatives 1-6 featuring a number of dipeptide residue bound to the glyoxylyl bridge, that is Phenylalanine-Leucine, Valine-Leucine, Leucine-Valine, L-Isoleucine-L-Valine, L-Isoleucine-L-Isoleucine, L-Valine-L-Isoleucine in their methyl ester form. N H O O HN R1 O NH R2 O O 1-6 R1=R2= -CH2-C6H5, -CH-CH3, -CH-CH3,-CH2-CH-CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3
36
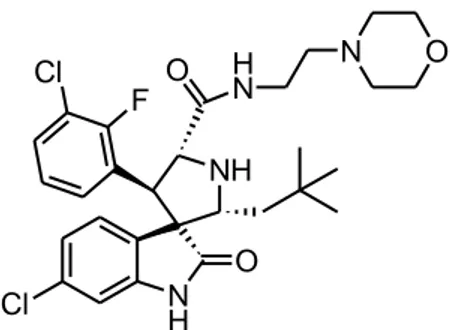
Molecular modeling was performed with the aim of revealing, at an atomic level, the potential interactions that govern the recognition and the binding of these compounds to MDM2. These calculations were performed using the publish co-crystal ligand Mi-63 (Figure 23), a MDM2-p53 interaction inhibitor belongs to the class of spiro-oxindole.
Cl N H O NH F Cl H N O N O
Figure 23. Chemical structure of Mi-63.
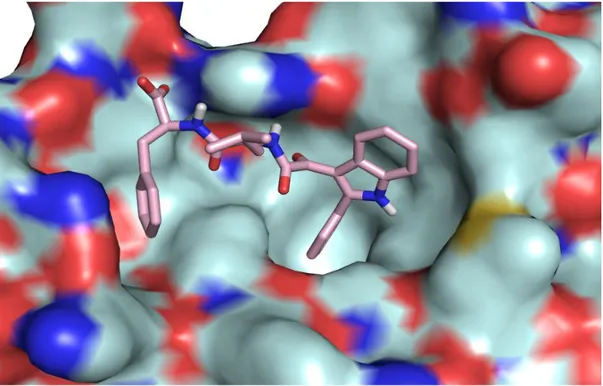
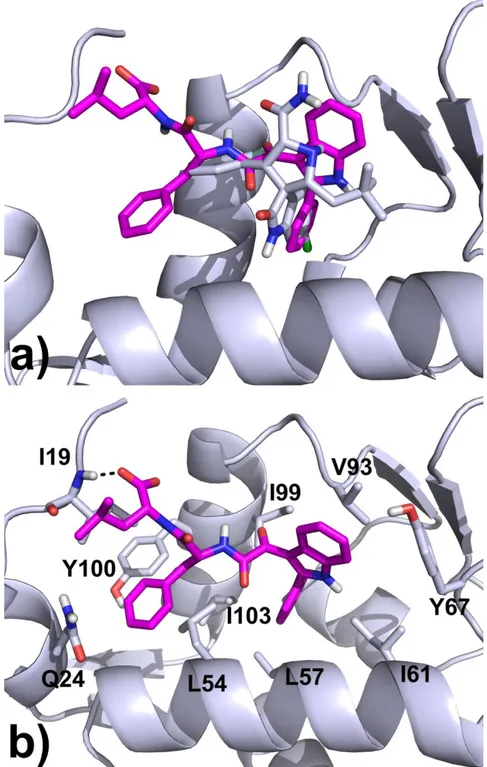
In the lowest energy docked conformation of compound 1, the phenyl ring attached to the indole core occupies the buried lipophilic pocket in the active site, establishing several hydrophobic interactions with the L57, I61, I99 and I103 side chains, while the indole ring contacts the V93 side chain and forms a T-shaped interaction with the Y67. The benzyl and the isobutyl groups of the dipeptide moiety adapt themselves in an extra pocket which is not occupied by the Mi-63 inhibitor (Figure 24). Here, other hydrophobic contacts are formed with the L54, I103, Y100 and I19 side chains. Moreover, the final carboxylate group engages an H-bond with the NH backbone of the I19 residue. Docking calculations of the other dipeptide analogues 2-6 give superimposable binding modes, perfectly superimposed with the one described for 1 (data not shown).
37
Figure 24. a) Superimposition of binding mode found for compound 1 with the Mi-63 analogue co-crystallized in the MDM2 enzyme (PDB code: 3LBL). b) Docking pose of 1 in the MDM-2 protein: ligands carbon atoms are displayed in magenta, key binding site residues as lightblue sticks. H-Bonds are shown as black dotted lines.
Another possible modification of the 2-phenylindol-3-glyoxylamide scaffold may be represented by the introduction on the amide side of a Phenylalanine and a Leucine at the position 5 of the indole nucleus (compound 7).
38 N H H N O O HN O NH2 7 O O
The synthesis of compounds 1-6 was reported in Scheme 1.
The commercially available 2-phenylindole was acylated with oxalyl chloride, in anhydrous ethyl ether, at 0°C to obtained the corresponding 2-phenylindolylglyoxyl chloride 8 which was allowed to react with the appropriate dipeptides (L-Phenylalanine-L-Leucine, L-Valine-L-(L-Phenylalanine-L-Leucine, L-Leucine-L-Valine, L-Valine, L-Isoleucine-L-Isoleucine, L-Valine-L-Isoleucine) in their methyl ester form, in the presence of triethylamine in dry toluene at room temperature for 20-24 hours (TLC analysis). At the end of the reaction, the suspension was filtered and the collected precipitates were washed with a 5% NaHCO3 aqueous solution and collected again to give products 1-6, that were
purified by washing with cold ether. Their structures were confirmed by 1HNMR and elementary analysis. (Experimental section)
39 Scheme 1 O O HN R1 O N H R2 O O O° C N H N H O O Cl ClCOCOCl anh. Et2O anh. Toluene Et3N , 0°C R1=R2= -CH2-C6H5, -CH-CH3, -CH-CH3,-CH2-CH-CH3. CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CF3COOH H2N R1 N H R2 O O O 8 N H 1-6
40
The key intermediate for the synthesis of compound 7 is the 5-nitro-2-phenylindole 9 that was obtained by nitration of the commercially available 2-phenylindole with NaNO3 in
H2SO4 at 0°C for 10 minutes. Scheme 2 N H NaNO3 / H2SO4 N H O2N 9 0°C
The synthetic procedure for the preparation of 7 is reported in Scheme 3. The acylation of 5-nitrophenyindole 9 with oxalylchloride, in anhydrous ethyl ether yielded the corresponding 5-nitrophenylindolylglyoxylyl chloride 10 which was allowed to react with L-Phenylalanine in its ethyl ester form, in the presence of triethylamine in dry toluene solution at 0°C for 20-24 hours (TLC analysis). At the end of the reaction, the suspension was filtered and the collected precipitate was washed with a 5% NaHCO3 aqueous solution
and collected again to give product 11, which was catalitically hydrogenated to yield the corrisponding amine 12, subsequently condensed with the Boc-Leucine in dry DMF and in presence of CDI yielding compound 13. Simple deprotection of the Boc group with trifluoroacetic acid in anhydrous CH2Cl2 gave the target compound 7. The reaction yields
41 Scheme 3 N H O2N O2N N H Cl O O ClCOCOCl Et2O , O°C N H O2N O O HN O O anh. Toluene NEt3 , 0°C H2N O O N H H2N O O HN O O H2 Pd/C abs. Ethanol CDI , DMF O N H O COOH N H H N O O HN O O O N H O O N H H N O O HN O O O NH2 CF3COOH CH2Cl2 13 12 11 10 9 7