CASE
REPORT
–
OPEN
ACCESS
InternationalJournalofSurgeryCaseReports81(2021)105805
ContentslistsavailableatScienceDirect
International
Journal
of
Surgery
Case
Reports
j o ur na l h o m e p a g e :w w w . c a s e r e p o r t s . c o mSurgical
stabilization
of
severe
flail
chest
with
Judet
and
Sanchez-Lloret
plates.
A
case
report
Alessandro
Stefani
a,∗,
Francesco
Tormen
a,
Adriana
Scamporlino
a,b,
Pamela
Natali
a,
Giorgio
Cavallesco
c,
Uliano
Morandi
aaDivisionofThoracicSurgery,UniversityofModenaandReggioEmilia,Modena,Italy
bClinicalandExperimentalMedicinePhDProgram,UniversityofModenaandReggioEmilia,Modena,Italy cDivisionofThoracicSurgery,UniversityofFerrara,Ferrara,Italy
a
r
t
i
c
l
e
i
n
f
o
Articlehistory: Received5March2021 Accepted18March2021 Availableonline22March2021
Keywords: Thoracictrauma Flailchest Surgery Casereport
a
b
s
t
r
a
c
t
INTRODUCTION:Flailchestisnowusuallytreatedbyconservativemethodsandsurgicalfixationremains
indicatedinselectedcases.Differenttechniquescanbeusedforfixation.Theaimofthispaperisto
presentacaseinwhichJudetandSanchez-Loretplateswereemployedandtodiscusstheusefulnessof
thistraditionaltechnique.
PRESENTATIONOFCASE:A79-year-oldwomanwasadmittedforleftthoracictraumawithsevere
antero-lateralflailchest.ShewasaffectedbyCOPDwithchronicrespiratoryfailure,ischemicheartdisease,
autoimmunethrombocytopeniatreatedonchronicsteroidtherapyandsevereosteoporosis.CT-scan
detectedmultipleribfractures,lefthemothoraxandlungcontusions.Aninitialconservativetreatment
offlailchestinvolvedcompressivebandageandtheninternalpneumaticstabilizationinICU,butitfailed.
Thepatientunderwentsuccessfulsurgicaltreatmentoftheflailchestbyfixationoftheanteriorfractures
fromthesecondtotheeightrib.JudetandSanchez-Lloretplateswereused.Abilateralpneumonia
developedduringtherehabilitationperiodandthepatientdiedtwomonthsafteroperation.
DISCUSSION:JudetandSanchez-Lloretplatesrepresentatraditionaltechniqueforfixationofflailchest.
Thistechniqueislessandlessusedandprogressivelyreplacedbynewermaterials,especiallytitanium
plateswithscrewsorintramedullarystruts.Ourpatienthadmultiplecomorbiditiesandaveryfragile
bonesthatadvisedagainstuseofscrewsorintramedullarystruts.
CONCLUSION:JudetandSanchez-Lloretplatescanbestillconsideredausefultoolforthefixationofflail
chestincasesofthinandfragilebones.
©2021TheAuthors.PublishedbyElsevierLtdonbehalfofIJSPublishingGroupLtd.Thisisanopen
accessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1. Introduction
Flailchest(FC)isdefinedasasegmentofthechestwallmoving paradoxicallywithrespecttotherestofthechestwallduring res-piration,resultingfrommultiplebifocalfracturesoftheribs.FCcan bealife-threateningcondition,leadingtoacuterespiratorydistress syndrome[1].SurgicalfixationofFChasnevergainedwidespread acceptanceandthemanagementofFChasgraduallychangedover theyears,asaconsequenceoftheimprovementinventilatoryand intensivecaretechniques.Therefore,themainstayofFCtreatment hasshiftedfromsurgicalstabilizationtowardsmoreconservative methods[2,3].However,thereareevidencessuggestingthat
surgi-∗ Correspondingauthorat:DivisionofThoracicSurgery,UniversityofModena andReggioEmilia,ViadelPozzo71,41120,Modena,Italy.
E-mailaddresses:[email protected](A.Stefani),
[email protected](F.Tormen),[email protected]
(A.Scamporlino),[email protected](P.Natali),[email protected](G.Cavallesco),
[email protected](U.Morandi).
caltreatmentremainsthebestoptionforFCinselectedcases[4–7]. Thesearethecasesinwhichtherespiratorydistressismainlydue totheparadoxicalmovementsofthechestwall,andthepatient cannotbeweanedfromthemechanicalventilation[8].
Theaimofthesurgicaltreatmentistheresolutionofthe para-doxicalmovementofchestwallthroughribfixation.Awidevariety oftechniqueshasbeenreportedand severaldifferentmaterials havebeenused,suchasplates,barswithorwithoutscrews,struts, wiresandsplints[9–13].Inthispaperwedescribeacaseofasevere FC,inaseverely-illpatient,successfullyfixedwithJudetplates(JP) andSanchez-Lloretplates(SLP).Theaimofthisreportistoshow thatthistraditionaltechnique,farfrombeingconsideredobsolete, remainsasimple,safeandeffectivemethodforFCstabilization.
ThisworkhasbeenperformedinlinewithSCAREcriteria[14].
2. Casepresentation
A79-year-oldwomanwasadmittedtotheEmergency Depart-mentforabluntthoracictraumafromanaccidentalfall.Shewasa
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.105805
2210-2612/©2021TheAuthors.PublishedbyElsevierLtdonbehalfofIJSPublishingGroupLtd.ThisisanopenaccessarticleundertheCCBY-NC-NDlicense(http://
CASE
REPORT
–
OPEN
ACCESS
A.Stefani,F.Tormen,A.Scamporlinoetal. InternationalJournalofSurgeryCaseReports81(2021)105805
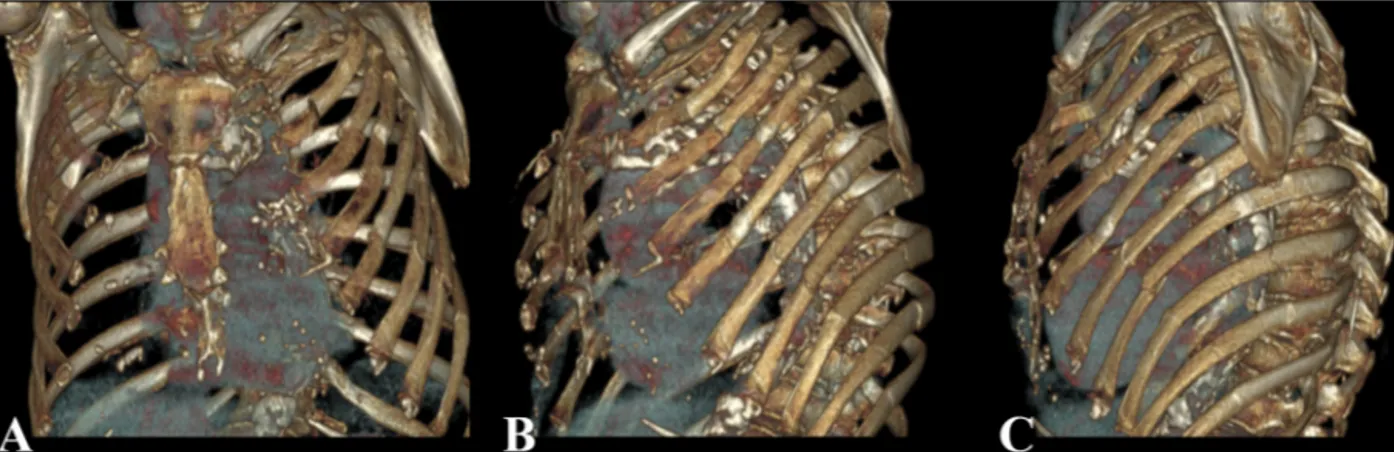
Fig.1.Three-dimensionalCT-scanreconstructionsshowingmultipledoubleortripleribfracturesfromthesecondtotheeightrib,withcrushingoftheanterolateralchest wall,andsinglefracturesoftheninthandtenthrib.
formerheavysmokeraffectedbyCOPDonchronicrespiratory fail-ure,treatedwithlong-termoxygentherapy.Shewasalsoaffected bymildrenalfailure,ischemicheartdisease,autoimmune throm-bocytopenia treated withlong-term steroidtherapy and severe osteoporosis.Onphysicalexamination,asevereleftanterolateral FCwaspresent.Chestx-raysdetectedmultipleribfracturesonthe leftside,fromthesecondtothetenthrib.CT-scandetectedaleft hemothoraxandmultiplelungcontusionsandpreciselyidentified thesiteand thenumber ofribfractures(Fig.1a,b,c).The emer-gencytreatmentrequiredaclosed-tubethoracostomy,allowingthe evacuationof1300ccofblood,andbloodtransfusion.Thepatient wastransferredinourUnitandtheFCwasinitiallytreatedwith aconservativeapproachbyexternalstabilizationwitha compres-sivebandage.Aprogressiveimpairmentoftherespiratoryfunction wasobservedduringthefirstweek,requiringadmissiontotheICU. Aftertwodaysofnon-invasiveventilationthepatientwas intu-bated.BecausetheFCwasstillunstable,atreatmentwithinternal pneumaticstabilizationwasstartedandcontinuedfortwoweeks. Duringthistime,pulmonarycontusionsprogressivelydisappeared, atelectasiswassuccessfullytreatedwithrepeatedbronchial aspi-rations and a tracheostomywas performed.However,repeated attemptstoweanthepatientfromtheventilatorysupportfailed, duetothepersistentsevereinstabilityoftheleftchestwall. There-fore,thepatientunderwentsurgicalfixationoftheFC,onemonth afterthehospitaladmission.
Ananterolateralthoracotomywasperformedalongthefourth intercostal space. The serratus anterior muscle insertions were dividedfromthesecondtotheseventhrib;a shortsegment of theanterioraspectoflatissimusdorsiandofthelateralaspectof pectoralismajorweresectioned.Thepleuralcavitywasentered throughthefifthintercostalspaceandexploredthrougha thoraco-scope.Six-hundredmloffluidandaresidualclottedhemothorax wereevacuated.Nootherlesionswerefound.Twopleuraldrains werepositionedbeforestartingthecostalstabilizationAllthe ante-riorfractureswerefixed,fromthesecondtotheeighthrib.The ribs wereexposed, in orderto obtaina goodplacement of the metalplates;thedissectionwasperformedonlyinthesiteofthe fracture,preservingtheintegrityoftherestoftheintercostal mus-cle.Thedislocatedsegmentsweremanuallyreduced.Thedouble anteriorfracturesofthesecondandfourthribwerefixedwitha SLP(oneforeachrib),whilethesingleanteriorfracturesofthe third, fifth,sixthandseventhribswerefixedwithaJP(onefor eachrib).Toreachtheanteriorfractureoftheeighthribasecond shortincisionwasneeded,caudallytothethoracotomy,andthe fracturewasfixedwithaJP.Oncethemetalplateswereplaced, theywerereinforcedwithaheavynon-absorbablesutureateach anchoringsite(Fig.2).Chestwallwasclosedinlayers,anda com-pressive bandage wasapplied.The operationtimewas90 min.
Fig.2. Intra-operativepicturesattheendoofthefixation,showingthemetallic platesinplace:twoSLPonthesecondandfourthribandsixJPonthethird,fifth, sixth,seventhandeightrib.Thesuturesaroundtheplatesarealsovisible,twofor eachplate.
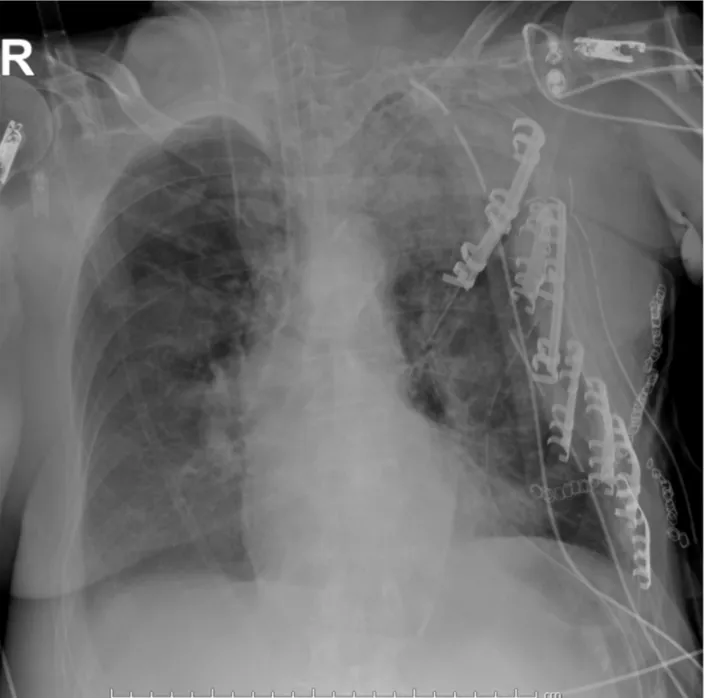
Postoperativechest-x-rayshowedthecorrectpositioningofthe plates(Fig.3).Mechanicalventilationwascontinuedforthreedays andthenweaningwasstarted.Theweaningwascompletedintwo weeksandthepatientwassupportedthroughnon-invasive ven-tilationforsevendaysmore.Noparadoxicalmovementoftheleft chestwallwasobservedduringspontaneousrespirationandthe chestwalladequatelyexpanded.ThepatientlefttheICU49days aftertheadmissionand wassent toaninpatient rehabilitation facility.Arespiratorysupportwithahigh-flownasalcannulawas initiallynecessary,thenthesupportwasshiftedtoconventional oxygentherapy,similartothatpreviouslyrequiredbythepatient. Unfortunately,anunexpectedbilateralpneumoniadeveloped dur-ingrecovery,witharapiddeteriorationoftherespiratoryfunction. ThepatientwasreadmittedtotheICUanddied6daysafter,thatis 3monthsafterthetrauma.
3. Discussion
Currently,it iscommonfor patientswithFCtobemanaged withnon-surgicalmethods,suchasconservativemethods (exter-nalcompressive bandage of the chest, pain control, aggressive pulmonary physiotherapy,non-invasive ventilation) or internal
CASE
REPORT
–
OPEN
ACCESS
A.Stefani,F.Tormen,A.Scamporlinoetal. InternationalJournalofSurgeryCaseReports81(2021)105805
Fig.3. Post-operativechestroentgenogramshowingtheleftchestarmormadeofmetallicplates.
pneumatic stabilizationthroughinvasivemechanicalventilation [8,15].Althoughsurgicalfixationofflailsegmentshasnevergained widespreadacceptance,thereisnowevidencethatitmaybe indi-catedinselectedcases[4–6].Arecentmeta-analysisbyApampa andcolleaguesincludedfourrandomizedcontrolledtrialsof surgi-calversusnon-surgicaltreatment[7]:lowermortality,lowerrisk ofpneumonia,reducedneedoftracheostomyanddecreased dura-tionofmechanicalventilationandICUstaywerefoundasaresultof fixation,comparedtonon-surgicaltreatment.However,although thepublishedliteratureonsurgicalfixationhasbeenrapidly grow-ing,thistechniqueremainsunfamiliartomostsurgeonsanditnow seemstobeunderutilized[16,17].
Itisgenerallyacceptedthatsurgicalfixationmaybeindicatedin patientspresentingwithanacuterespiratorydistresswhichneeds aventilatorsupport,providedthatsuchaclinicalconditionis def-initelysustainedbytheparadoxicalmovementsoftheFC[8].In thiscase,oncetherespiratoryandhemodynamicconditionsofthe patienthavebeenstabilized,theoperationshouldnotbedelayed. Ifotherlunginjuriesorclinicalconditionssignificantlycontribute
totherespiratorydistress(i.e.pulmonarycontusions)and/ortothe needofmechanicalventilation(i.e.cerebrallesions),aconservative treatmentshouldbepreferred[18].Thesurgicaltreatmentshould beconsideredafterallothertraumaticlesionshavedisappeared buttheFCremainsunstableanditisidentifiedastheonlypossible causeofapersistentrespiratorydistress,intheabsenceofother clinicalconditionscontraindicatinganoperation.Ourcasebelongs tothissecondclinicalscenario.Theoperationwasdelayedforafew daysbecauseofseveralco-morbiditiesofthepatient.Moreover, thesevereosteoporosisandlong-termsteroidtherapycouldhave madethefixationtroublesomeorevenineffective.Thishigh oper-ativeriskledustoanextremeattempttoweanthepatientfrom themechanicalventilation,beforeproposingsurgicalintervention. Manydifferenttechniqueshavebeendescribedforribfixation, eitherintramedullaryorexternaltothefracturedbones.Usually, notallthefracturesofaFCrequirefixationtoachievestabilization [7].Inourpatientthefixationoftheanteriorfractureswas ade-quatetostabilizetheFC.Agreatvarietyofmaterialsforfixation hasbeenproposed.Judetplates(forsimplefractures)and
CASE
REPORT
–
OPEN
ACCESS
A.Stefani,F.Tormen,A.Scamporlinoetal. InternationalJournalofSurgeryCaseReports81(2021)105805
Lloretplates(forcomminutedfractures)havebeenusedinthepast [9,13,19],butcurrentlytheyaremuchlessemployedandreplaced bynewermaterials,suchascontouredtitaniumplatesfixedtothe ribswithscrewsorintramedullarysplints[12].Butourpatientwas oldandonlong-termsteroidtherapyandshewasaffectedbysevere osteoporosis.Ribswerethinandextremelyfragile.Screwswould nothaveprobablyheldonandintramedullarysplintswouldhave brokenthebonefromtheinside.ThisiswhywedecidedtouseJP andSLP.Theplateswereplacedoverthefracturelineand,by grad-uallybendingthelateralhooks,theyprogressivelygraspedtherib andwerefirmlyanchoredtothebone.Thus,inthiscomplexcase,JP andSLPprovidedasimple,quickandeffectivefixationoffractured ribswithoutfurtherfracturingordamagingthebone.
4. Conclusions
SeveraldifferentmaterialsareavailableforribfixationofaFC. Atpresenttitaniumplatessecuredwithscrewsrepresentthe pre-ferredtechnique,whileJPandSLParelessandlessused.However, thetraditionaltechniqueusingthis typeofmaterialcanstillbe useful,especiallyincasesofthinandfragilebone.
DeclarationofCompetingInterest
Theauthorsreportnodeclarationsofinterest.
Sourcesoffunding
Thisresearchdidnotreceiveanyspecificgrantfromfunding agenciesinthepublic,commercial,ornot-for-profitsectors.
Ethicalapproval
Ethicalboardapprovalisnotrequiredforasinglecasereportin ourCenter.
Consent
Writteninformedconsentwasobtainedfromthepatientfor publicationofthiscasereportandaccompanyingimages.Acopy ofthewrittenconsentisavailableforreviewbytheEditor-in-Chief ofthisjournalonrequest.
Authorcontribution
FrancescoTormenandPamelaNatalicollecteddata.
AlessandroStefaniandFrancescoTormenwrotethemanuscript. AdrianaScamporlino,GiorgioCavallescoandUliano Morandi revisedandapprovedthemanuscript.
Registrationofresearchstudies
Notapplicable.
Guarantor
AlessandroStefaniistheguarantorofthisstudy.
Provenanceandpeerreview
Notcommissioned,externallypeer-reviewed.
References
[1]B.T.Flagel,F.A.Luchette,R.L.Reed,T.J.Esposito,K.A.Davis,J.M.Santaniello,
etal.,Half-a-dozenribs:thebreakpointformortality,Surgery138(2005)
717–723.
[2]G.C.Clark,W.P.Schecter,D.D.Trunkey,Variablesaffectingoutcomeinblunt
chesttrauma:flailchestvspulmonarycontusion,J.Trauma28(1988)298.
[3]M.Freedland,R.F.Wilson,J.S.Bender,M.A.Levison,Themanagementofflail
chestinjury:factorsaffectingoutcome,J.Trauma30(December(12))(1990)
1460–1468.
[4]A.J.M.Cataneo,D.C.Cataneo,F.H.S.DeOliveira,K.A.Arruda,R.ElDib,P.E.De
OliveiraCarvalho,Surgicalversusnonsurgicalinterventionsforflailchest,
CochraneDatabaseSyst.Rev.29(2015),CD009919.
[5]R.B.Beks,J.Peek,M.B.deJong,K.J.P.Wessem,C.F.Oner,F.Hietbrink,etal.,
Fixationofflailchestormultipleribfractures:currentevidenceandhowto
proceed.Asystematicreviewandmeta-analysis,Eur.J.TraumaEmerg.Surg.
45(2019)631–644.
[6]J.A.Leinicke,L.Elmore,B.D.Freeman,G.A.Colditz,Operativemanagementof
ribfracturesinthesettingofflailchest:asystematicreviewand
meta-analysis,Ann.Surg.258(2013)914–921.
[7]A.A.Apampa,A.Ali,B.Kadir,Z.Ahmed,Safetyandeffectivenessofsurgical fixationversusnon-surgicalmethodsforthetreatmentofflailchestinadult populations:asystematicreviewandmeta-analysis,Eur.J.TraumaEmerg. Surg.(2021),http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00068-021-01606-2,published online6Feb2021.
[8]H.Pan,S.B.Johnson,Bluntandpenetratinginjuriesofthechestwall,pleura,
diaphragm,andlungs,in:J.LoCiceroIII,R.H.Feins,Y.L.Colsono,G.Rocco
(Eds.),Shield’sGeneralThoracicSurgery,8thedition,WoltersKluver,2018,
chapter110.
[9]R.Judet,Costalosteosynthesis,Rev.Chir.Orthop.ReparatriceAppar.Mot.59
(Suppl.1)(1973)334–335.
[10]J.Borrelly,G.Grosdidier,B.Wack,Surgicaltreatmentofflailchestbysliding
staples,Rev.Chir.Orthop.ReparatriceAppar.Mot.71(1985)241–250.
[11]R.J.Landreneau,J.M.HinsonJr.,S.R.Hazelrigg,J.A.Johnson,T.M.Boley,J.J.
Curtis,Strutfixationofanextensiveflailchest,Ann.Thorac.Surg.51(1991)
473–475.
[12]M.Bottlang,W.B.Long,D.Phelan,D.Fielder,S.M.Madey,Surgical
stabilizationofflailchestinjurieswithMatrixRIBimplants:aprospective
observationalstudy,Injury,Int.J.CareInjured44(2013)232–238.
[13]H.Tanaka,T.Yukioka,Y.Yamaguti,S.Shimizu,H.Goto,H.Matsuda,etal.,
Surgicalstabilizationorinternalpneumaticstabilization?Aprospective
randomizedstudyofmanagementofsevereflailchestpatients,J.Trauma52
(2002)727–732.
[14]R.A.Agha,M.R.Borrelli,R.Farwana,K.Koshy,A.Fowler,D.P.Orgill,Forthe
SCAREGroup,TheSCARE2018statement:updatingconsensusSurgicalCAse
REport(SCARE)guidelines,Int.J.Surg.60(2018)132–136.
[15]N.Dehghan,C.deMestral,M.D.McKee,etal.,Flailchestinjuries:areviewof
outcomesandtreatmentpracticesfromtheNationalTraumaDataBank,J.
TraumaAcuteCareSurg.76(2014)462–468.
[16]J.C.Mayberry,L.B.Ham,P.H.Schipper,etal.,SurveyedopinionofAmerican
trauma,orthopedic,andthoracicsurgeonsonribandsternalfracturerepair,J.
Trauma66(2009)875–879.
[17]J.D.Richardson,G.A.Franklin,S.Heffley,etal.,Operativefixationofchestwall
fractures:anunderusedprocedure?Am.Surg.73(2007)591–597.
[18]B.L.Pettiford,J.D.Luketich,R.J.Landreneau,Themanagementofflailchest,
Thorac.Surg.Clin.17(2007)25–33.
[19]D.DiFabio,D.Benetti,M.Benvenuti,G.Mombelloni,Surgicalstabilizationof
post-traumaticflailchest.Ourexperiencewith116casestreated,Minerva
Chir.50(March)(1995)227–233.
OpenAccess
ThisarticleispublishedOpenAccessatsciencedirect.com.ItisdistributedundertheIJSCRSupplementaltermsandconditions,which permitsunrestrictednoncommercialuse,distribution,andreproductioninanymedium,providedtheoriginalauthorsandsourceare credited.