RevPortCardiol.2018;37(4):351.e1---351.e4
www.revportcardiol.org
Revista
Portuguesa
de
Cardiologia
Portuguese
Journal
of
Cardiology
CASE
REPORT
Autonomic
cardiovascular
control
and
cardiac
arrhythmia
in
two
pregnant
women
with
hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy:
Insights
from
ICD
monitoring
Pietro
Francia
∗,
Carmen
Adduci,
Beatrice
Musumeci,
Lorenzo
Semprini,
Francesca
Palano,
Luigi
Zezza,
Massimo
Volpe,
Camillo
Autore
DepartmentofClinicalandMolecularMedicine,St.AndreaHospital,SapienzaUniversity,Rome,Italy
Received19December2016;accepted11September2017 Availableonline17April2018
KEYWORDS Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; Pregnancy; Implantable cardioverter defibrillator;
Heartratevariability; Ventricular
arrhythmia
Abstract In women with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), pregnancy prompts major
changes inhemodynamicandcardiacautonomicfunction thatmay precipitateheart failure (HF)orincreasetheriskofcardiacarrhythmia.
Wereporttheclinicalfollow-upoftwopatientswithnon-obstructiveHCMimplantedwitha cardioverterdefibrillator(ICD)allowingforcontinuousanalysisofheartrate(HR),heartrate variability(HRV)andcardiacarrhythmiathroughouttheentirecourseofpregnancy.
BothpatientsexperiencedincreasedHRanddecreasedHRVfromtheearlystagesof preg-nancy, whichpersisteduntil delivery.Prematureventricularcontractions(PVCs)andrunsof non-sustainedventriculartachycardia(NSVT)reachedapeakinthesecondandthirdtrimesters, concurrentwithsympathetichyperactivity.InonepatientwithbaselineNYHAclassIIHF symp-toms,increasedPVCsandNSVTwereconsistentwiththedeterioration ofHF,supportingthe decisiontobringthedeliveryforward.Whilebothpatientsexperiencedapersistentincrease in sympathetic tone and ventricular ectopic activity, no life-threatening arrhythmias were documented.
Duringpregnancy,patientswithhypertrophiccardiomyopathydevelopprogressive neuroauto-nomicimbalance,promptinganincreaseinnon-sustainedventriculararrhythmia.Thisenhanced arrhythmiaburdenwarrantsclosefollow-upandrhythmassessmentduringthethirdtrimester, especially inwomen who have heart failuresymptoms before pregnancy. Implantable car-dioverter defibrillatorsprovideacontinuousanalysisofheartratevariabilityandarrhythmia burdenthatsupportstherapeuticdecision-makingduringfollow-up.
© 2018SociedadePortuguesade Cardiologia.Publishedby ElsevierEspa˜na,S.L.U.Allrights reserved.
∗Correspondingauthor.
E-mailaddress:[email protected](P.Francia).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repc.2017.09.019
351.e2 P.Franciaetal. PALAVRAS-CHAVE Miocardiopatia hipertrófica; Gravidez; Cardioversor-desfibrilhador implantável; Variabilidadeda frequênciacardíaca; Arritmiaventricular
Controlecardiovascularautonómicoearritmiacardíacaemduasgestantes
commiocardiopatiahipertrófica:observac¸õespormeiodomonitoramentocomCDI
Resumo Em mulheres com miocardiopatia hipertrófica, a gravidez aumenta as variac¸ões
hemodinâmicas e as alterac¸ões da func¸ão autonómica cardíaca que podem provocar insu-ficiênciacardíaca ou aumentaro risco dearritmia. Reportamoso acompanhamento clínico de duaspacientescom miocardiopatia hipertróficanão obstrutiva, ambas implantadascom cardioversor-desfibrilhador(CID).A monitorac¸ãocomCIDpermiteaanálisecontínuada fre-quênciacardíaca,davariabilidadedafrequênciacardíaca(VFC)edaarritmiadurantetodaa gravidez.AsduaspacientesmanifestaramaumentosdaFCediminuic¸õesdaVFCdesdeoinício dagravidezatéaoparto.Observou-se umpicodefrequênciadeextrassístolesventriculares (EV)edetaquicardiasventricularesnãosustentadas(TVNS)nosegundoeterceirotrimestres dagestac¸ão,emcorrespondênciadahiperatividadesimpática.Numadaspacientescomclasse funcionalNYHAII,antesdagravidez,oaumentode EVedeTVNScontemporaneamente ao agravamentodainsuficiênciacardíacalevouàdecisãodeanteciparoparto.Asduaspacientes demonstraramumaumentopersistentedaatividadesimpáticaedaatividadeectópica ventric-ular,nãoexistiramcasosdearritmiasventricularesmalignas.Duranteagravidezaspacientes commiocardiopatia hipertróficadesenvolvem um progressivodesequilíbrio autonómico que causaumaumentodasarritmiasventricularesnãosustentadas.Oaumentodoriscoarrítmico necessitade um constanteefrequente controleclínico edo ritmocardíaco duranteo ter-ceirotrimestre,especialmenteemmulherescomsintomasdeinsuficiênciacardíacaantesda gravidez.Ocardioversor-desfibrilhadorimplantávelforneceumaanálisecontinuada variabili-dadedafrequênciacardíacaedasarritmiasquepodemapoiarasdecisõesterapêuticasdurante agravidez.
©2018SociedadePortuguesadeCardiologia.PublicadoporElsevierEspa˜na,S.L.U.Todosos direitosreservados.
Background
Maternaldeathisrareinpregnantwomenwithhypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM).However,thedeteriorationof clini-calconditionsmayoccurinasmallbutsignificantproportion ofpatients1.Pregnancypromptsmajorchangesin
hemody-namicandcardiacautonomicfunctionthatmayprecipitate heart failure or increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia. Thispaperreportstheclinicalanddevicefollow-upoftwo patients with non-obstructive HCM implanted with a car-dioverterdefibrillator (ICD),thereby providingcontinuous analysisofheartrate(HR),heartratevariability(HRV)and cardiac arrhythmia throughout the entire course of preg-nancy.
Case
report
Patient A had been diagnosed with HCM at the age of 14and implantedwith asingle-chamber ICD(Maximo VR, Medtronic) at the age of 22 based on massive left ven-tricular(LV)hypertrophy(>30mmmaximalwallthickness), non-sustainedventricular tachycardia(NSVT)anda family historyof unexplained sudden deathin a first-degree rel-ative<50 yearsof age2,3.She underwenta life-savingICD
intervention for ventricular fibrillation (VF) at the age of 26.
Atweek1ofpregnancyshewas30yearsold,hadNYHA classIIsymptomsandwasontreatmentwithatenolol50mg daily.Duringpregnancy,sheunderwentroutineclinicaland
ICDfollow-upvisitseverytwotothreemonths.AteachICD interrogation, HR trends, HRV (expressed as SDNN, stan-dard deviation of normal-to-normal RR intervals), single premature ventricularcontractions (PVCs),series of PVCs (2---4beats),runs ofNSVT(>4beats)andatrial fibrillation (AF)episodeswererecorded.
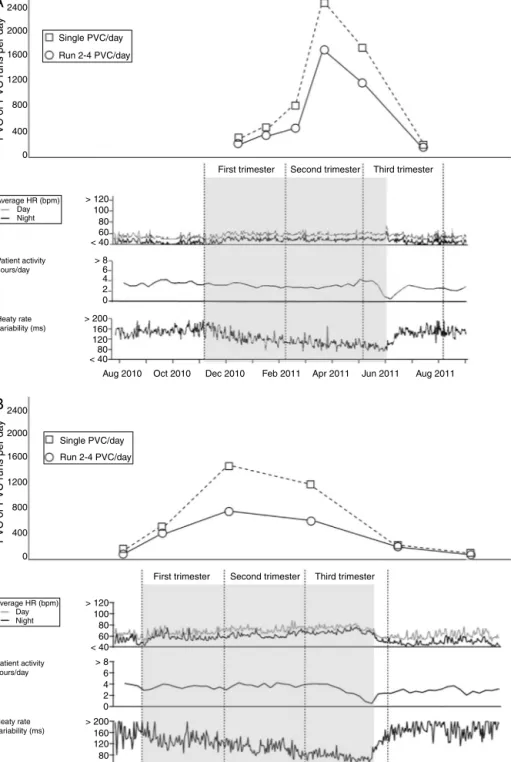
Data retrieved from the ICD showed increased HR and decreased SDNN from the early stages of pregnancy (week4),withapeakandplateauinthesecondandthird trimesters (Figure, panel A). She experienced eight runs of NSVT between week 12 and week 30, together with a substantial increaseof single PVCs(from 280 to2500 per day onaverage) andseriesofPVCs(from190 to1500 per day on average) from week 18 that persisted until deliv-ery (Figure, panelA).The patientdidnot experienceany episodes of AF. Compared to baseline, during the third trimester, patientA experiencedprogressive worseningof heartfailuresymptoms(transitionfromNYHAclassIItoIII), increased pulmonary artery pressure(PAP) asassessed by Dopplerechocardiography(from30mmHgto45mmHg)and increasedventricularectopicactivity,asrecordedbytheICD (Figure,panelA).Asaresult,cesareandeliverywas sched-uled at week 30and thepre-term infantwastemporarily admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit. Drug ther-apydidnotchangethroughoutfollow-up.AtICDfollow-up (12weeksafterdelivery),HR,SDNNandPVCswerefoundto beatpre-pregnancylevels.
Patient Bhad been diagnosed with HCM at the age of 12andimplantedwithaprimarypreventionsingle-chamber ICD (Entrust VR, Medtronic) at the age of 30 based on
Neuro-autonomicdriveandarrhythmiainHCMduringpregnancy 351.e3
A
2400 PVC or PVC r uns per da y PVC or PVC r uns per da y 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 2400 > 120 Average HR (bpm) Patient activity hours/day Heaty rate variability (ms) Day Night Average HR (bpm) Patient activity hours/day Heaty rate variability (ms) Day Night > 8 > 200 160 120 80 < 40 Aug 2010 Single PVC/day Run 2-4 PVC/day Single PVC/day Run 2-4 PVC/dayFirst trimester Second trimester Third trimester
First trimester Second trimester Third trimester
Oct 2010 Dec 2010 Feb 2011 Apr 2011 Jun 2011 Aug 2011 6 4 2 0 100 80 60 < 40 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 > 120 100 80 60 < 40 > 8 > 200 160 120 80 < 40
Nov 2013 Jan 2014 Mar 2014 May 2014 Jul 2014 Sep 2014 Nov 2014 6
4 2 0
B
Figure1 PVC,PVCseries,HR,dailyactivity(hours)andHRV(SDNN)throughouttheentirecourseofpregnancyasretrievedfrom theICDmemoryinpatientA(panelA)andpatientB(panelB).
ThenumberofPVCsisshownatthemidpointbetweentwocloseclinicalevaluationsandICDfollow-upvisits.
PVC,prematureventricularcontraction;HR,heartrate;HRV,heartratevariability;SDNN,standarddeviationofnormal-to-normal RRintervals.
massiveLVhypertrophyandNSVT2.Sheneverexperienced
ICDinterventions.
At week 1 of pregnancy, Patient B was 37 years old, asymptomatic,andonatenolol,25mgdaily.
She underwentroutineclinical andICD follow-upvisits throughoutpregnancy(everytwotothreemonths).Ateach ICD interrogation, HR trends, HRV, single PVCs, series of
PVCs,runsofNSVTandatrialfibrillation(AF)episodeswere retrievedfromtheICDmemory.
Duringpregnancy, data retrievedfrom the ICDshowed increasedHRanddecreasedSDNNfromweek4withapeak andplateauinthethirdtrimester(Figure,panelB).Patient BexperiencedanincreaseinsinglePVCs(from34to1400per dayonaverage)andseriesofPVCs(from70to500perday
351.e4 P.Franciaetal. onaverage)fromweek 16untildelivery (Figure, panelB).
Duringthethirdtrimester,shedidnotexperienceany dete-riorationofheartfailuresymptomsorAFepisodes,andPAP remainedwithinthenormalrange(max.26mmHg).Atenolol wasnotup-titratedduringfollow-up.Thepatientunderwent uncomplicatedcesareandeliveryatweek34after oligohy-dramnios.Thebabywasborningoodhealth.Duringroutine ICDfollow-up10 weeksafterdelivery,HR,SDNNand ven-tricularectopicactivitywerefoundtobeatpre-pregnancy levels.
Discussion
In healthy women, pregnancyis associated with hemody-namic and cardiac autonomic changes4. Indeed, HR rises
asacompensatory response toreducedsystemic vascular resistanceandHRV decreases duetoa shiftin autonomic balancetowardssympathetichyperactivity5.Theextentto
whichthisoccursinpregnantwomenwithHCMandwhether itmayaffect theriskof cardiacarrhythmiaandprognosis is currently unknown. For the first time, we used an ICD forcontinuousbeat-to-beatanalysisofHR,HRVandcardiac arrhythmiathroughouttheentirecourseofpregnancyintwo high-riskHCMpatients.
HRVanalysisshowedapersistentriseinsympathetictone earlyinpregnancy.Ontheonehand,fluctuationsinplasma estrogenandprogesteronemayexplaintheincreased sym-pathetic outflow that, in turn, triggers PVCs and NSVT as a result of beta-adrenergic stimulation of the hyper-trophic myocardium. On the other hand, the increase in ventricularectopicactivitymayoccurasaresultof disease-relatedfailuretocompensatefor expanded blood volume and tachycardia, particularly in the context of massive LV hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction. Irrespective of whetherenhancedectopicactivityisprimaryorsecondary inorigin,cardiacrhythmassessmentisreasonable evenin the early stages of pregnancy in HCM patients. Nonethe-less, sympathetichyperactivity, PVCs and NSVTshowed a peakin the second andthird trimesters,concurrent with maximumvolumeoverload, HR,cardiacoutputand circu-latingcatecholamines.Thismarkedincreaseinventricular arrhythmiawasconsistentwithdeteriorationofheart fail-uresymptomsandsupportedthedecisiontoanticipatethe deliveryin patientA. Accordingly,closeclinical follow-up includingrhythmassessment iswarrantedin HCMpatients during the third trimester, especially in women who are symptomaticbeforepregnancy.Heartfailuresymptomsand cardiac arrhythmia may indicate the need for cesarean and/orearlydelivery.
Finally, while both patients experienced a persistent increaseinventricularectopicactivity,nolife-threatening arrhythmiawasdocumented.Thisisconsistentwithprevious studiesthathaveshownthatsustainedventricular arrhyth-mia isuncommon in pregnantwomen withHCM,and that PVCsandNSVTdonotpredictpersetheriskofdeath1,6,7.
Conclusions
During pregnancy, patients with hypertrophic cardiomy-opathy develop progressive neuroautonomic imbalance promptinganincreaseinnon-sustainedventricular arrhyth-mia. This enhanced arrhythmia burden warrants close follow-upandrhythmassessmentduringthethirdtrimester, especially in women who have heart failure symptoms before pregnancy. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators provide a continuous analysis of heart rate variability andarrhythmiaburdenthatsupportstherapeutic decision-makingduringfollow-up.
Conflict
of
interest
Dr. Pietro Francia served as consultant and received speaker’sfeesfromBostonScientific.
References
1.AutoreC,ConteMR,Piccininno M,etal. Riskassociatedwith pregnancyinhypertrophiccardiomyopathy.JAm CollCardiol. 2002;40:1864---9.
2.Maron BJ,Maron MS.ContemporaryStrategies for Risk Strati-ficationand PreventionofSuddenDeathwiththeImplantable Defibrillator in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2016.
3.BosJM,MaronBJ,AckermanMJ,etal.Roleoffamilyhistoryof suddendeathinriskstratificationandpreventionofsuddendeath withimplantabledefibrillatorsinhypertrophiccardiomyopathy. AmJCardiol.2010;106:1481---6.
4.DuvekotJJ,PeetersLL.Maternal cardiovascularhemodynamic adaptationtopregnancy.ObstetGynecolSurv.1994;49:S1---14.
5.MoertlMG,UlrichD,PickelKI,etal.Changesinhaemodynamic and autonomous nervous system parameters measured non-invasivelythroughoutnormal pregnancy.EurJObstetGynecol ReprodBiol.2009;144Suppl1:S179---83.
6.PieperPG,WalkerF.Pregnancyinwomenwithhypertrophic car-diomyopathy.NethHeartJ.2013;21:14---8.
7.FranciaP,SantiniD,MusumeciB,etal.Clinicalimpactof non-sustainedventriculartachycardiarecordedbytheimplantable cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with hypertrophic car-diomyopathy.JCardiovasElectrophysiol.2014;25:1180---7.