Xenopus laevis embryos
In order to obtain embryos, Xenopus females were pre-injected with 100 units of pregnant serum gonadotrophin (Folligon) 4-11 days prior to egg collection, and with 800-1000 units of human chorionic gonadotrophin (Gonasi HP 5000, Serono) the night before collection.
The next day, eggs are obtained by gently squeezing the frogs and then fertilized with testis homogenates. The embryos are cultured in 0.1X MMR. After half an hour from fertilization, jelly coats are removed keeping the embryos for several minutes in dejelling solution. Embryos were staged according to Nieuwkoop and Faber (Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1967).
Solutions: MMR NaCl 0,1 M KCl 2 mM MgSO4 1 mM CaCl2 2 mM HEPES 5 mM pH 7.8 EDTA 0,2 M Dejelling solution DDT 3,2 mM Tris-HCl 0,2 M pH 8.8
Transformation of Competent E. coli
To obtain a large amount of plasmid DNA we added the DNA to the competent cells (E. coli, DH5) basically following protocols provided by the “ Molecular cloning” manual (Sambrook J et al., 1998).
Purification of plasmid DNA
Plasmid DNA was extracted from bacterial cells (E. coli, DH5) by alkaline lysis and purified by chromatography through Nucleobond columns (Macherey- Nagel). Plasmids DNA were lipofected or linearized and used as templates for antisense probe or capped mRNA transcription.
Constructs
Plasmidic vectors
Plasmic vectors used to transcribe antisens dig RNA in in situ hybridization experiments are:
• pBluescript KS e SK.(gene bank “52327”, “52329”) • pGEM3 (Promega)
• pCMV-SPORT6 (Invitrogen)
The espression vectors used in the lipotransfectio experiment are: • pCS2+ plasmid.
Although originally designed for expressing proteins in Xenopus embryos from either injected RNA or DNA, pCS2+ is also useful for high-level transient expression in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. pCS2+ contains a strong enhancer/promoter (simian CMV IE94) followed by a polylinker and the SV40 late polyadenylation site. A SP6 promoter is present, allowing in vitro RNA synthesis of sequences cloned into the polylinker. A T7 promoter in reverse orientation is present between the polylinker and the SV40 polyA site for probe synthesis, as well as a second polylinker after the SV40 polyA site to provide several possible sites to linearize the vector for SP6 RNA transcription. The vector backbone is from pBluescript II KS+ and includes the amp resistance gene and an f1 origin for producing single stranded DNA. A number of derivatives of pCS2 have been constructed that allow fusions to epitope tags (i.e.:
Myc-tag) and other marker proteins, as well as nuclear localization signals (http://sitemaker.umich.edu/dlturner.vectors/home).
• pCS2MT+
Used to produce fusion proteins, includes 6 copies of myc epitope reconnise by a monoclonal Ab 9E10. (http://sitemaker.umich.edu/dlturner.vectors).
- pCS2MTXXgadd45γ vector has been gently gave by Prof. Gomez-Skarmeta (CSIC, Madrid).
- pCS2MTXcdk2 and pCS2MTXciclinaA2, have been previously used in lipotrasfected experiments by (Casarosa et al., 2003)
Plasmidic clones
The following plasmid clones were used to performe the in vitro transcrition of sonde used for the in situ hybridization or lipotransfectin experiments:
° Xath5 (Harris and Perron, 1998) cDNA cloned in pBluescript . To transcribe, we used the T7 polymerase after enzymatic restriction with NotI .
° Xbh1 (Patterson et al., 1998) cDNA is cloned in pGEM-3Z. This plasmid contains a 1000 bp insert corresponding to Xbh1 cDNA except the two first aa. It is contain about 110 bases of its 3’UTR. To transcribe, we used the SP6 polymerase after enzymatic restriction with EcoRI (Poggi et al., 2004)
° XE2F in pCS105 (constructed by David Hsu) was a generous gift of Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou (Rockefeller University, New York, United States)
° GFP sensors were obtained by cloning RT-PCR fragments of the 3’ UTRs into XhoI-XbaI sites of pCS2-GFP
° Xvsx1 gene bank BC044049; Xvsx1 cDNA fragment (2994 pb) is inserted in pCMV-SPORT6. To transcribe, we used the T7polymerase after enzymatic restriction with Sal1
° XcycD1 (Casarosa et al., 2003); XcycD1 cDNA is inserted in pBluescript KS. T3. To transcribe, we used the T3.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with BamHI
° Xhermes (Gerber et al., 1999); Xhermes cDNA fragment (1.3 Kb) is inserted in pBluescript SK. Il clone di hermes che noi abbiamo utilizzato non è completo, ma non si hanno 400 basi al 5’ terminale. To transcribe, we used the T7.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with BamHI
° Xirbp (Gonzalez-Fernandez et al., 1993); XIrbp cDNA (888 pb) is inserted in pCMV-SPORT6. To transcribe, we used the T7.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with EcoR5
° XN-tubulina (Richter et al., 1988); XN-tub cDNA (1.7 Kb) is inserted in pBluescriptKS. To transcribe, we used the T3.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with NotI
° Xotx5b (Viczian et al., 2003); Xotx5 cDNA (1.65K Kb) is inserted in pBluescriptSK. To transcribe, we used the T7.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with NotI
° Xotx2 (Viczian et al., 2003); Xotx2 cDNA (900 bp) is inserted in pGEM3. To transcribe, we used the SP6.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with EcoRI
° Xgadd45γ (de la Calle-Mustienes et al., 2002); Xgadd45γ cDNA is inserted in PGEM-T. To transcribe, we used the Sp6.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with KspI ° Xrx1 (Casarosa et al., 1997). Xrx1 (1485 bp) is inserted in pGEM3. To transcribe, we used the T7.polymerase after enzymatic restriction with BamHI
Istology
Embryos were fixed in 4% PFA for 30 min up to 2 h at room temperature and successively were placed in PBS with 30% sucrose, to minimize freeze. After an overnight incubation at 4 ºC or 3 hr at RT the PBS/sucrose solution was dried, and embryos were embedded in the Tek OCT blocks and fastly freezed at -80 ºC.
Solutions: PBS 1X: NaCl 13,7 mM KCl 22 mM Na2HPO4 80 mM KH2PO4 15 mM
pH 7.4
More embryos in single block were cutted with Leica C1850 cryostat to obtain transversal sections with a thickness of 10-12 μm. Section are collected in SuperFrost slide and save at -80°C untill their use .
Antibodies
Following antibodies have been used in the immunoisthochemistry experiments: Primary antibodies:
- Anti-Brdu (5-bromo2-deossiuridin): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (B2531); monoclonal antibody; used dilution (1:500).
- Anti-calbindin: produced by oncogene; catalog number (PC253L); policlonal antibody developped in rabbit; diluizione di utilizzo (1:500). Used to reveal cones (Chang and Harris, 1998).
- Anti-GFP (green fluorescent protein) policlonal: produced by chemicon; catalog number (AB3080); caming from jellyfish Aequorea victoria; used dilution (1:200). - Anti-myc-tag (policlonale): produced by MBL; catalog number (562); policlonal antibody; used dilution (1:500). Used to reveal XGadd45γ XciclinaA2-Xcdk2, Xchx10 espression.
- Anti-myc-tag (monoclonal): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (M5546); sviluppato in topo; used dilution (1:500). Used as above.
- Anti-pH3 (fosfo-histone): produced by upstate; catalog number (06-570); policlonal antibody develop in rabbit; used dilution (1:400). Used to reveal mitotic cells in different animal species
- Anti- acetylated tubulin: produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (T6793); monoclona antibody produced in mouse. Used to reveal neural processes of post-mitotic neurons; used dilution (1:500).
- Anti GABA (DiaSorin; 1:1000), anti 5-HT (DiaSorin; 1:1000), anti-tyrosine hydroxilase (DiaSorin; 1:1000), R5 (1:100, kindly supplied by W. Harris) used to reveal amacrin cells
- Xvsx1, Xotx5b, and Xvsx1 antibodies, immunoaffinity-purified polyclonal antibodies were generated in rabbit by PRIMM antibodies (see below)
Secondary antibodies:
- Anti-rabbit IgG (whole molecule): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (T6778); developed in capra; used dilution (1:150); Ab coniugated with (TRIC tetrametilrodamina isotiocianato).
- Anti-mouse IgG (whole molecule): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (C2181); developed in sheep; used dilution (1:200); Ab coniugated with (CY3….); reagisce con le sottoclassi IgG di tipo G1, G2a, G2b, G3.
- Anti-mouse IgG (whole molecule): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (F2883); developed in sheep; used dilution (1:100); Ab coniugated with (FITC fluoresceina isotiocianato).
- Anti-rabbit IgG (whole molecule): produced by Sigma-Aldrich; catalog number (F1262); developed in capra; used dilution (1:64); coniugated with (FITC).
Immunocytochemistry
Cryostat sections (12 µm) were washed three times for 5 minutes in 1X PBS + 0.1% Triton X-100 (PBST), then incubated 1 hour at 37°C with primary antibody: anti-calbindin (Merck Biosciences, 1:1,000), anti-5-HT (DiaSorin, 1:1,000), anti-GABA (DiaSorin; 1:1,000), anti-tyrosine hydroxilase (DiaSorin; 1:1,000), R5 (1:100, kindly supplied by W. Harris [University of Cambridge, United Kingdom]), anti-GFP (MolecularProbes, 1:500).
Sections were washed in PBS three times for 5 minutes and incubated with a 1:500 dilution of the appropriate fluorophore-conjugated (oregon green, rhodamine) anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies (Molecular Probes; 1:500) 37°C for 1 hours. The sections were washed again in PBS and mounted.
To immunodetect Xvsx1, Xotx5b, and Xvsx1 proteins, immunoaffinity-purified polyclonal antibodies were generated in rabbit by PRIMM SRL. Synthetic peptides (three for each of Xvsx1 and Xotx5b, and two for Xotx2), corresponding to 15aa long regions outside the homeobox of the predicted protein sequence, were used as immunogens. Antibody specificity was first assayed by Western blot analysis. Immunostaining of HEK 293T cells, transfected with the coding sequence of the three genes, confirmed the specificity of all three antibodies. The following antibodies were used: anti-Xotx5b (1:10), anti-Xotx2 (1:200), anti-Xvsx1 (1:100). Anti-Xotx2
antibodies was incubated as described, except anti-Xotx5b (0.3% instead of 0.1% Triton X-100) and anti-Xvsx1 (antigen unmasking by 15-min treatment with 2N HCL).
Western blotting
Protein samples were loaded onto a 12% polyacrylamide gel for size separation. Subsequently, proteins were transferred to Immobilon-P Tranfer membrane (Millipore) by electroblotting for 1-2 hours. Blots were blocked for 1 hour using 5% nonfat dry milk in TBS-T [10 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0; 150 mM NaCl; 0.05% (v/v) Tween-20 (Sigma)]. Monoclonal primary anti-MYC antibody (Sigma) (dilution 1:500) and secondary anti-mouse IgG (peroxidase conjugate) were used to detect MYC-tagged proteins. Filters were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature for each antibody, and then washed three times with TBS-T to remove excess antibody. The Super Signal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Pierce) was used to visualize immunoreactive bands by exposure to Amersham Hyperfilm. Samples from at least two independent experiments were analyzed.
BrdU experiments
Different stage embryos (30, 33-34, 37-38, 42) injected with BrdU (5-bromo-2- deoxyuridine, Roche) in the gut, were fixed at different time and later (dependently by the study to perform on) cryostat sectioned. In situ hybridization or immunostaining was performed on 12 µm sections as described above; after that, sections were stained for BrdU. To do this, sections were washed with 2N HCl for 20 minutes then neutralized with several PBST washes. The anti-BrdU antibody (Molecular Probes) was added at 1: 500 dilution and incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes. After three changes of PBST, Cy3 goat anti-mouse (Chemicon) secondary antibody was added at 1: 1000 dilution and incubated for 45 minutes at 37°C. The samples were washed three times with PBST and stained with 15 mg/ml Hoechst solution for 3 minutes at room temperature, to visualize nuclei. After three final washes in PBST, sections were mounted in Aqua Polymount .
Hydrossiurea/Aphidicolin (HUA) treatments
Embyos were treated starting from stage 30, 33/334, 35/36 until stage 42 in 0.1X MMR containing 20 mM hydroxyurea and 150 μM aphidicolin (HUA, Harris and Hartenstein,
1991; Hardcastle and Papalopulu, 2000) until fixation. The effect of hydroxyurea and aphidicolin treatment on cell division was examined as described previously (Andreazzoli et al., 2003).
Hydroxyurea is able to blok the nucleoside diphosphate reductase, an enzime catalising the ribonucleotides redox in deossiribonucleotides, fondamental event in DNA biosintesis. Aphidicolin instead is an inhibitor, of the eucariotic DNA polimerase.
This inhibitors combination of DNA syntesis has been used because hydroxyurea affects DNA syntesis in a briefly time ( about 2 hours), but it cannot completely inhibits it, while aphidicolin starts its activity in a slow time (about 4-6 hours) and together with hydroxyurea completely block DNA synthesis.
Syntetic RNA synthesis
Capped mRNA in vitro synthesis
The capped mRNA were obtained using the mMessage mMachineTM Sp6 kit (AMBION), following the instructions provided by the company. After DNAse digestion to remove template DNA, the RNAs were purified in phenol-chloroform and ethanol precipitated. The concentration of the RNA was estimated by agarose gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometry. Aliquots were then stored at -80 °C.
Antisense labelled probes synthesis
Standard RNA synthesis from linearized plasmids using Sp6, T7 or T3 RNA polymerases were carried out incorporating a digoxigenin or fluorescein conjugated ribonucleotide. In particular, transcription reactions were performed in the presence of 1mM each of ATP, CTP and GTP, 350 M UTP and 650 M DIG-11 UTP or Fluo-12 UTP for 2 hrs at 37 °C (Dig mix Roche).
After DNAase digestion to remove template DNA, the RNAs were purified in phenol-chloroform and ethanol precipitated or in RbCl 5M e 1V di isopropanol forr 15 minutes at -80°C. After a briefly centrifugations at 12000 rpm at 4°C for 20 minutes followed from a successively centrifugation at 12000 rpm in 100 μl of a precooled EtOH 70% at 4° for 5 minutes, the concentration of the RNA was estimated by agarose gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometry. Probes were then diluted in hybridisation mix at the final stock concentration of 10 µg/ml and stored at -20 °C for several months.
Hybridization techniques
In situ hybridisation on sections
Dissected and fixed embryos in 4% PFA for 30 min up to 2 h at room temperature were placed in PBS with 30% sucrose, to minimize freeze. After an overnight incubation at 4 ºC the specimen from the PBS/sucrose solution, placed in the Tek OCT and fastly freezed at -80 ºC.
Embryos were cryostat-sectioned to be further processed for in situ hybridisation. Cryostat sections were thawn and dried at room temperature. In situ hybridisation was performed as follows. On the first day, sections were incubated overnight in probe mix (1-0,1 μg/ml hybridisation mix) at 65 °C in a humified chamber (50% formamide, 1X salts). Next day, sections were washed 30’ for 3 times at increasing stringency in washing solution to eliminate the unbound probe which may lead to background. After two washes, 30’ each, in MABT, the sections were incubated for two hrs at RT in blocking solution. After this time, they can be incubated in antibody solution overnight at RT.
The unbound antibody must be removed with 5 washes, 30’ each, in MABT. To reveal the hybridized probe, sections were washed twice for 10’ in Alkaline Phosphatase Buffer (APB), pH 9.5 supplemented with 2mM Levamisole (SIGMA), an inhibitor of endogenous phosphatases. For the chromogenic reaction, sections are incubated in NBT-BCIP or Fast red AP substrate (Roche) until the staining reaches the desired intensity.
Whole-mount in situ hybridization
By means of this technique, it is possible to detect mRNA localization onto the whole embryo. Niehrs’ protocol was preferred because it is more sensitive than others and gives little or no background. Staged embryos were fixed in MEMFA for 1 hour at room temperature, gradually dehydrated and stored in ethanol at -20 °C. On the first day of the whole mount protocol, the embryos were gradually rehydrated in PBTw (PBS containing 0,1% Tween-20), treated with 10 μg/ml Proteinase K for 5’ and refixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 20’. After washing in PBTw, the embryos were prehybridased for at least two hours in hybridisation mix at 60-65°C. Then, embryos were incubated overnight in probe mix (50 ng of antisense labeled RNA probe diluted in 600 μl of hybridisation mix was the working concentration).
The next day, embryos were washed at growing stringency to eliminate the unbound probe which may lead to background.After recovering the probe (it can be recycled over time), the embryos were washed twice for 30’ in SSC 2X, CHAPS 0,1 % at 37 °C and then twice for 30’ in SSC 0,2X, CHAPS 0,1 % at 60-65 °C. After two washes, 10’ each, in TBSTX (TBS containing 0,1% Triton-X 100) the embryos were incubated for two hrs at 4 °C in blocking solution; in the meantime, also the antibody (diluted in blocking solution; 1:2500 anti-DIG or 1:8000 anti-fluo) was incubating at 4°C on a rocker. After this time, the embryos were incubated in antibody solution for four hours at room temperature or overnight at 4 °C.
The unbound antibody must be removed with 5 washes in TBSTX. One should be done overnight at 4 °C, the others are 1 hr each at room temperature.
To reveal the probe, the embryos were washed twice for 10’ in Alkaline Phosphatase Buffer (APB), pH 9.5 supplemented with 2mM Levamisole (SIGMA), an inhibitor of endogenous phosphatases. For the chromogenic reaction, embryos were incubated in BM-Purle or fast red AP substrate (Roche) until the staining reached the desired intensity (from some hours to several days, depending on the “strength” of the probe and the expression levels of the gene under analysis).
Solutions: Hybridization buffer Formammide 50% Sali 10X 1X Denhardt’s 1X Destran solfato 50%
MABT (Maleic Acid Buffer Tween) pH 7.5 Acido maleico 100 mM NaCl 150 mM Tween-20 0,1% AP buffer Tris 100 mM pH 9.5 MgCl2 50 mM
NaCl 100 mM Tween-20 5 mM Levamisol 2 mM 10X Salts (1L) NaCl 114 g Tris HCl 14,04 g Tris Base 1,34 g NaH2PO4*2H2O 7,8 g Na2HPO4 7,1 g 0,5M EDTA 10 ml
Xenopus laevis embryos lipofections
Using this technique, single retinal progenitors can be transfected in vivo at different stages of retinal differentiation. This technique has been previously described in the Xenopus embryo CNS by (Holt et al., 1990). Lipotransfection is a usefull protocol to study cell-autonomu effects in genes expressed during the retinogenesis (Holt et al., 1990). Using this technique is possible to study the gain- and loss-of function of an interested gene in singol retinal progenitors in a wild-type contest.
It has been estimated that translation of the lipofected plasmids occurs after 6/8 hours after transfection (Dorsky et al., 1997), thus a certain control of timing of expression is possible. CNS
DNA isolated by Nucleobond midi preps was diluted in nuclease-free water to a concentration of 2 mg/ml. These stocks were spun down for at least 10 minutes at 4°C before use. 1 µl of each construct was mixed with 1 µl pCS2+GFP (green fluorescent protein) DNA to label the progeny of transfected cells. pCS2+GFP alone was used as the control. DOTAP (N-[1-(2,3-diolielossi) propil]-N,N,N-trimetilammonio metilsolfato; Roche) was added to DNA in a ratio of 1µg to 3 µ l. The mixture was then injected into the presumptive eye region of stage 17-18 or stage 25-26 embryos using a nanoject apparatus (Drummond) (Fig. 1A). At stage 42, embryos were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 1 hour at room temperature and sunk in 30% sucrose overnight at 4°C. Embryos were then embedded in O.T.C.TM compound (Sakura), freezed and cryostat sectioned (10 µm). Samples were rehydrated with two washes of 1X PBS for 5
minutes, mounted in Aqua Polymount (Polysciences) and dried overnight at room temperature before microscope analysis.
Niddles imployed in lipofection and injection experiments were pulled using a classic “Puller” for elettrofisiology (Sutter Instruments Co; parametri: heat 95, pull 50), starting from glass capillars (Drummond). Before to set up the microinjector the niddle was broken under the binocular microscope with a pair of Dumont n. 5, to obtain a niddle top of about 20 ,40 µm: at this point the niddle is empty with mineral oil and charged with 3-4 µl of a cDNA-DOTAP mix.
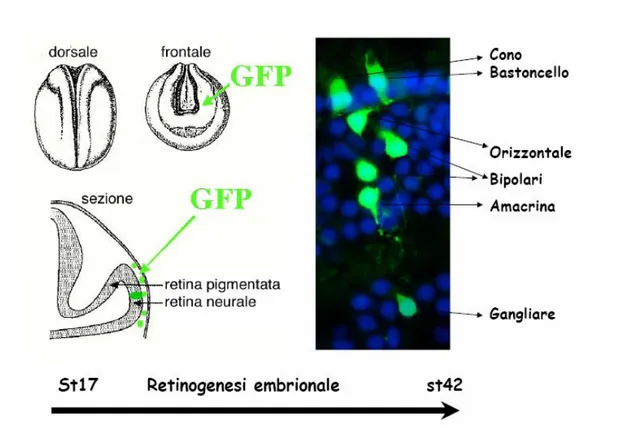
Fig. 12. Lipotrasfection technic.
The scheme illustrates the lipofection technique performed on Xenopus embryos (st. 17). Single progenitors are transfected with a DNA construct + GFP. At the end of retinogenesis (st. 42), the clones derived from lipofected progenitors are analysed (in green). Nuclei are stained with Hoechst (in blu).
Visualization and analisys of lipofected cells
Lipotransfected embryos at stage 17-18 were fixed, sezionattd and generally analizzed at stage 42, corresponding at a mature embryonal retina completely stratified. In the sectioned retine were analyzed cells expressing the reporter gene Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), o il myc-tag coespressed together with the lipofected protein. GFPis a protein spontaneusly fluorescent isolated from the Pacific jellyfish Aequorea victoria. Its function is to translate in vivo, the blue chemioluminescence to discriminate lipotransfected cells using a simple epifluorescent miscroscope. Myc is not a fluorescent protein and for this reason we performed an immunostaining using a primary and secondary antibody against it. Beeing fluorescent the secondary antibody can be analysed under an epifluorescent microscope. Cell types have been distinguished by thier morphology and specifc localization in three distinct cell layers; this last point is facilitated by colourating cellular nuclei with hoechst fluorocrome.
Microinjection of in vitro transcribed mRNA
125-400 pg of several capped RNA + a reporter gene (pCS2+GFP, β-gal) were injected into a dorsal blastomier onto the animal region of 4-cell-stage embryos, using a Drummond ‘Nanoject’ apparatus. Embryos were injected in 0.1X MMR and 4% Ficoll-400 (Sigma), and grown up overnight at 14°C in the same solution. Next day embryos ficoll-400 were changed in 0.1X MMR leading their growth until the desiderate stage. As controls wt animal, sibling embryos were grown in the same 0.1X MMR.
Statistic treatment of data
Cellular types
For each lipofected constructs, the ratio of every specific cell type, respect to the total number of counted cells, has been calculated on a thousand cell samples, coming from several lipofected retine. n, in the results, rapresent the total cell number counted for each lipofected constructs. The percentage media has been calculated on minimum namber of three samples. For each percentage media were calculated the standard deviation and the standard error medium. SEM has been used for every confidence barrs of each showed isthogramms. Differences between two medie are considered
significative when up than alla somma delle loro SEM; this result is indicated by a stars uponat the error barrs on the top of the hystograms.
BrdU incorporation
In the BrdU incorporatin experiments it has been calculated the lipotransfected cells ratio of the BrdU-positive nuclei, respectto the total number of lipofected cells with BrdU-negatives nuclei. The statistical analysis has been performed as mentioned above. Tunel staining
Embryos were lipofected or injected with GFP and several pCS2 vectors, grown to stage 30, 33/34 or 37/38, fixed and cryostat sectioned. I used Intergen’s ApopTag Kit to stain apoptotic cell nuclei and counterstained with Hoechst (15 mg/ml). Retinas with at least one lipofected, apoptotic cell were counted. Several retinas were counted for each construct at each stage. The percentage of apoptotic lipofected cells versus all lipofected cells was determined.
RNA extraction and RT-PCR analysis
RNA extraction and RT-PCR were performed as described in Lupo et al. 2002.
- RT-PCR of Xenopus laevis dicer was carried out using forward 5’atgcatttcaagtgccatca and reverse 5’aaaagggacccattggagag primers.
microRNAs (miRs) identification
microRNA expression profiling
Initial studies indicate that miRNAs may regulate as much s 30 % of all genes in the genome, thus comprising a otally new level of gene regulation. miRNAs have already been found to play important roles in several types of cancers and in tissue differentiation.
The ability to monitor large changes in large numbers of miRNAs simultaneously is a key factor in understanding miRNA function. Exiqon has therefore developed the miRCURY™ LNA array system for large-scale investigation of miRNA expression. The capture probes used in the miRCURY™ LNA Arrays incorporate Exiqon’s highaffinity Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA™) technology. The incorporation of LNA™ into an oligonucleotide probe greatly increases the affinity of that oligonucleotide for
it’s complementary DNA or RNA target. For every LNA™ incorporated into an oligonucleotide, its melting temperature (Tm) when bound to target increases by 2 - 8° C. The features of the miRCURYTM LNA Array – high sensitivity, high specificity and Tm-normalized probes.
We will use miRCURY™ LNA microRNA Array slides. These slides contain capture probes complementary to mature miRNAs of many animal and plant species, in addition to a number of positive and negative control capture probes. This version of slides is an evolution of that we used to carry out preliminary experiments (see Preliminary Results). The slides contain 4 copies of a large panel of capture probes covering 92.3% of the miRNAs of all organisms annotated at present in the data base miRBase 9.0 (see http://www.exiqon.com). This version now includes 187 capture probes to Xenopus miRNAs (versus 105 of the previous version). Moreover, due to the high degree of evolutionarily conservation of the miRNAs sequence, it is possible that a capture probe for one different species can correspond to an as yet unidentified Xenopus miRNA, thus enhancing the potential of this analysis. For a more detailed description of the method, see also Results.
Locked nucleic acid-based in situ detection on section of miRNAs
The protocol used is focuses on the locked nucleic acids (LNAs) for sensitive and specific histological detection of microRNAs (miRNAs) by in situ hybridization (Gregor Obernosterer et al., 2007)
Locked nucleic acid-based whole-mount in situ detection of miRNAs
The whole mount protocol of ISH of miRNAs is a slightly modification of the Niehrs’ protocol (Wienholds et al., Science 309, 310-1, 2005; Kloosterman et al., Nat Methods 3, 27-9, 2006). The significant difference is the probe nature. We used 15-22 nt long, Dig-pre-labelled LNA™ probes (Exiqon), complementary to the target sequence of interest. Detection was carried out at RT by BMP purple staining for 24-36 hrs. Negative control probes did not significantly stain.
microRNAs loss of function experiments
Antisense 2'-O-methyl oligonucleotides to the mature sequence of miRNAs of interest were synthesised and directly lipofected using DOTAP. Lipofection was performed at st. 17-18 into optic vesicle, as described in Materials and Methods. pCS2-GFP plasmid was colipofected, as tracer. The best doses for injection/lipofection were established based on embryos viability and targeting efficiency.
For the experiments performed in this thesis work, we use the following Xenopus tropicalis sequences : xtr.decoy 155: ccccuaucacgauuagcauuaa xtr.decoy 129: gcaagcccagaccgcaaaaag xtr.decoy 222: aaccauacaaccuacuaccuca xtr.decoy 125b: ucccugagacccuaacuuguga xtr.decoy 122: acaaacaccauugucacacucca xtr.decoy let7c: aaccauacaaccuacuaccuca xtr.decoy 184: agccuuaucaguucuccgucca xtr.decoy 23b: gguaaucccuggcaaugugau xtr.decoy let7a: aacuauacaaccuacuaccuca
Microphotographs
The sectioned retinae have been analysed by means Nikon Eclipse 600, microscope harbor 4X, 10X, 20X and 40X optics. Brightfield images were performed using circular dichroism (DIC). Images have been acquired with a digital camera Photometrix, ”Cool Snap”, provide of a CCD colour sensor with a dynamic of 12 bit for each channel and 1,3 Mpixels resoluction.