MILAN POLITECHNIC UNIVERSITY
SCHOOL OF ARCHITECTURE, URBAN PLANNING AND CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERING MASTER OF SCIENCE IN MANAGEMENT OF BUILT ENVIRONMENT
BUSINESS SUSTAINABILITY AND BUILT ENVIRONMENT
The impact of green businesses in the residential housing sector: A path toward the implementation of the United Nation goal 7.
Supervisor: Prof. Massimiliano Guerini
Master Science Thesis of: Georges Tresor Doungala Matr: 897686
2
Thanksgiving
A special Thanks to my Supervisor Professor Massimiliano
A special Thanks to Professor Licia Sbatella and the Polimi Multichance team
A special Thanks to the foundation Samaja
3
Abstract
Green businesses are new forms of businesses that not only focus on building profits, but also pay attention to people and planet. As any other business companies, they might fail, being exposed to common economical and financial risks. These risks might represent a threat to the survival of those companies on the long run, impacting also their management operations.
The thesis objective is to investigate the problems that challenged the correct financial sustainability of high-risk profile companies operating in green businesses. At the hearth of this analysis, Tesla motors and Solar City. These two high risk profile green companies have as core vision the infusion of environmental sustainability principles in normal sectors such as transportation and energy utility. The reason of choice for this companies is without any doubt their transparency in their operations, the accessibility to financial, and managerial datas and most importantly the innovation in their way to handle and solve critical business issues in a sustainable way.
The results emerged from this cashflow analysis, suggest bankruptcy risk and solvency risk as the two major financial sustainability threats of high risks profile companies. The analysis enlightens the metrics that are to be monitored in order to keep the company financial situation under control. However, this analysis, also show that, a company can be bankrupt, or insolvent, but still has a high tangible asset value (property, plant, equipment) see fig 2, pag.18. A company who falls in one of these scenarios is therefore in a state in which, it has too much default to continue its operations, but at the same time too much value to close. Conglomeration merger appears therefore in that case, as a possible solution. An insolvent company will try to merge with a high liquidity profile company, and a bankrupt company will likely merge with a high equity profile one.
4
As the thesis continues further in investigation, the conglomerate merge of Tesla Motors and Solar City Corp is leading in the creation of a new materiality, which impact is leading to a drastic transformation on the built environment, particularly in the residential housing sector .The term “built environment”, is intended as places and spaces created or modified by people including buildings, parks, and transportation systems.
5
Summary
Thanksgiving ... 2
Abstract ... 3
Chapter 1: Introduction ... 7
Chapter 2: Green Businesses ... 9
2.1 : Tesla Motors INC ... 11
2.2 : Solar City Corp... 12
Chapter 3: Business Financial Sustainability ... 13
3.1 LIQUIDITY ... 14
3.2 Operating Efficiency (EBIT MARGIN) ... 14
3.3 Profitability ... 15
3.4 Solvency ... 16
3.5 Analysis of Solar city financial situation ... 17
Chapter 4: Vertical Integration as a Sustainability Mechanism ... 27
4.1 Definition of Vertical integration. ... 27
4.2 Solar city Corp ‘s acquisition by Tesla Motors: Vertical integration as sustainability mechanism. ... 29
Chapter 5: Impact of sustainability business on Built environment ... 32
5.1 Tesla Solar roof Analysis. ... 32
5.2 From Building Applied Photovoltaics (BAPV) to Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) ... 37
Chapter 6: Financial application of BIPV: SOLAR REITs. ... 41
6.A: Solar Project financing Structures ... 41
6.1. Special Purpose Vehicle Financing model ... 41
6.1.2 Project execution and management ... 44
6.2 Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) ... 46
6.B Solar Project Financing in the residential properties Sector ... 48
6.3 Warehouse for Energy Efficiency Loans (WHEEL) program ... 48
6.4 The CT Solar Loan for Homeowners Target. ... 49
6.C: The potential application of BIPV in the real estate industry: Solar REITS. ... 51
Chapter 7: Conclusion ... 53
References ... 55
Figures index ... 57
7
Chapter 1:
Introduction
According to the United nations development program (UNDP) sustainable report, in particularity on goal 7 implementation, it emerges the following facts:
• 2,9 billion of people use wood, coal, charcoal, agricultures residues or animal waste to cook their meals and heat their homes.
• 4 million people die from illness attributable to household air pollution from cooking with solids fuels.
• 1,1 billion people lacks access to electricity.
• There will be 70% projected growth of the word electricity demand.
According to the tracking Clean Energy Progress of June 2017, over 2 million of electric cars are on the road, and over 750.000 EVs sold worldwide in 2016.
According to the UN environment global statute report 2017, buildings and construction together account for 36 % of global final energy use, which 82 % was supplied by fossil fuels in 2015. It is relevant to note that:
• Buildings only on themselves account for 30 % of global consumption, from which 22% are in the residential sector. Transportation on the other side accounts for 28% of world energy consumption.
8
• In term of pollution, residentials buildings accounts directly for 6 % of CO2 emissions, and 11% indirectly.
These facts represent challenges that must be face for the good of the environment and for the human well beings. The solutions according to the goal 7, would be first, to ensure access to clean, reliable and modern energy to all, and secondly to invest in the dissemination of renewable energy use. The United nation has ensured to provide its support as a solution, to business and entrepreneurial skills development, enhancing access to small scale financing for renewable energy solutions. This measure has increased worldwide the green business sector also call sustainable business. The UNDP does extend his actions, in the supporting programs and policies, for the promotion to access to clean, affordable, reliable energy services for households, communities and businesses, and the promotion of renewable energy technologies, including Solar PV, mini Hydro power plants, solar water heaters……
The scope of our work is to explore how, 2 green business companies (Tesla and Solar City), in their attempt to reach business sustainability, are moving toward the implementation of the goal 7. It will be in the first case, to understand in chapter two, what is intended by green businesses, their characteristics, strategic practices, and used standards. In chapter three, after a brief description of the 2 companies under analysis, it will be the case to study which mechanism has been employed by them in order to maintain their financial survival (sustainability). The chapter four will provide, an analysis of these mechanism’s benefits for the built environment, leading us to a deep analysis of Building Integrated Photovoltaics technologies in chapter five. Finally, in chapter six, after an analysis on how PV technologies are financed, the thesis will try to demonstrate how Integrated PV technologies can provides a significant improvement, in the adoption and dissemination of clean and affordable energy for all.
9
Chapter 2:
Green Businesses
According to Wikipedia “A sustainable business also called green business, is any organization that participates in environmentally friendly or green activities to ensure that all processes, products , and manufacturing activities adequately address current environmental concerns while maintaining a profit .In other word it is a business that meets the needs of the present ( world) without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own. It is the process of assessing how the design products that will take advantage of the current environmental situation and how well a company’s products perform with renewable resources”.
Sustainable businesses goals are basically to meet the customer needs, considering the reduction of negative environmental effects, using a structural approach known also as Sustainable Enterprise Excellence concept. The structural approach is the result of technological solutions, tools and methods. Green businesses ultimate results are generally linked with the generation of greens energy, and the production of new materialities.
At the strategic level, sustainable businesses incorporate differents eco-practices in order to support their activities. The following list provides some employed strategies:
• Innovation and technologies • Process improvement
• Collaboration
• Sustainability reporting • Supply chain greening
10
Green businesses can be recognized by the 6 following characteristics according to
Matthew Tueth:
• Triple top-line value products generation • Nature based knowledge and technology
• Products of service to products of consumption • Solar, wind geothermal and ocean energy • Local based organizations and economies • Continuous improvement process
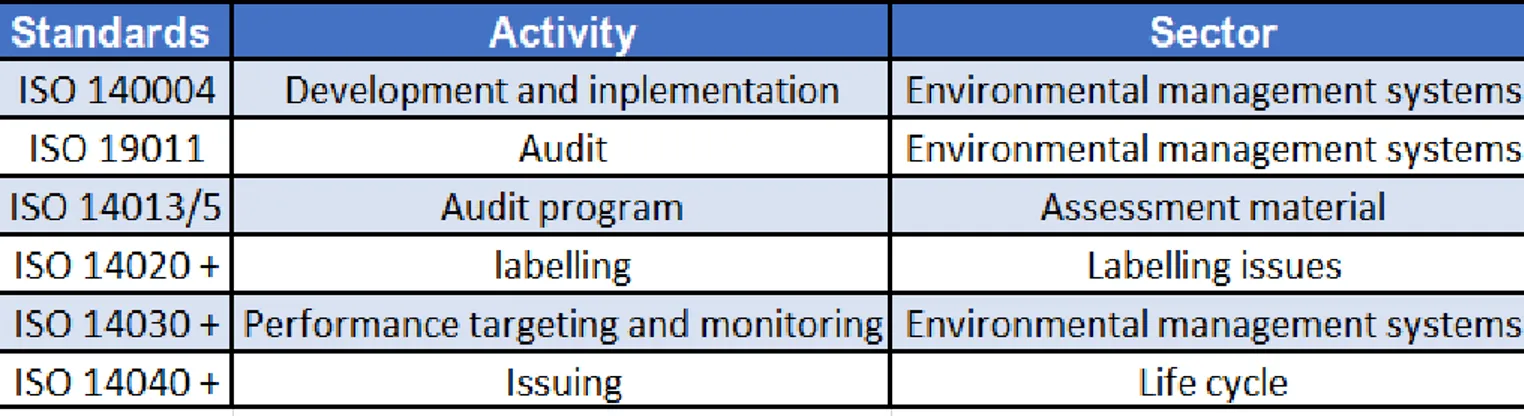
The table below contains some standards commonly used by green businesses.
11
There are other standards associated to the built environment, under the name of Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) standards. It is the most used green building rating system, providing and creating healthy, highly efficient and cost- saving buildings. The LEED certification is a recognition of a sustainable achievement through energy, water, resources, and waste, savings.
Among green businesses companies, two leaders will be particularly taken in consideration for the purpose of the thesis argument. The two companies are Tesla Motors, and Solar City Corp.
2.1
: Tesla Motors INC
Tesla Motors is an American automotive company based in Palo Alto in Canada. The company has been founded by engineers Martin Eberhard ( CEO) and Marc Tarpenning (CFO) , in July 1st 2003 .The company is specialized in electric car manufacturing .Tesla began its business by manufacturing cars for the sport industry before moving to mass market vehicles .The company first mass market car model was the roadster , followed by the model S and the recent model X , using the lithium ion battery cells.
In late 2007, Eberhard Martin both resigned as CEO and president of Technology, joining the advisory board, to finally leave the company in 2008. Tarpening vice president of the electrical engineering, left the company the same year. Elon Musk, cofounder of PayPal, who was also Tesla chairman, became the new CEO.
The technological strategy of Tesla relies solely on electric propulsion technologies. The production strategy incorporates a high degree of vertical integration instead of outsourcing.
12
with the aim to perform fast electrics cars charging, exceptionally free for Tesla cars.
According to Tesla Master plant, the scope of the company is to accelerate the world’s transition toward sustainable energy, by creating a “vertically integrated company that builds electric vehicles, batteries to store power and solar panels to generate power”.
2.2
: Solar City Corp.
According to the Solar Thermal magazine, “SolarCity is an American public company which is specialized in clean energy provision. The company has its headquarter in San Mateo, in California. Its primary activities include the design, the finance, and the installation of solar energy systems installation. The company is also involved in the execution of energy efficiency audits and building of charging stations for electric vehicles.”
In 2008, under the business suggestion of Elon Musk (ex-chairman of Tesla Inc), Peter and Randon Rive, (cousins of Elon) founded the company. The company adopted a leasing strategy with the purpose to decrease the cost of solar power installation. In 2009 the company made a significant move by entering in the electric car charging business. In 2010, the company expanded its client base and started stepping away from its initial market segment, providing services for homeowners. Clients now includes government, business, and nonprofit organizations. In May of the same year, the company realized the largest solar installation in San Francisco.
In 2011, the company announced a five-year plan that would see its investment more than one billion dollars in photovoltaics solar projects, targeting privately militarized communities.
13
Chapter 3:
Business Financial Sustainability
According to Financial Times, “Business sustainability is often defined as managing the triple bottom line. A process by which companies manage their financial, social and environmental risks, obligations, and opportunities. These three impacts are sometimes referred to as profits, people and planet. However this approach relies on an accounting based perspective , and does not fully capture the time element that is inherent within business sustainability .A more robust definition is that business sustainability represents resiliency over time .Business that can survive shocks because they are intimately connected to healthy economic , social and environmental systems. These businesses create economic value and contributes to healthy ecosystems and strong communities.”
The robust definition gives more emphasis on the survival aspects of companies. Two fundamentals points must be underlined, which are healthy economic and environmental systems. What is intended by healthy economy? And how is it related to companies? In other words, how do we measure the financial health of companies?
In order to measure the financial health and long-term sustainability of a company, some financials metrics should be taken in consideration. Those financial metrics can be divided into four areas which are, liquidity, solvency, profitability and operating efficiency.
14
3.1 LIQUIDITY
Liquidity is the amount of cash easily convertible to cash assets that a company owns to manage its short-term debt obligations. Two metrics used to measure liquidity are generally the current ratio and the quick ratio referred as the acid test. The quick ratio gives a more precise measure in the sense in which it provides a more realistic practical indication of a company’s ability to manage short term obligations with cash and assets on hand. A quick ratio greater than 1, indicates that a company is able enough to meet its short-term obligations. Another metric to monitor , in order to measure liquidity is the long-term debt. Companies with too much long-term debt, who find themselves in a liquidity crisis, risk having too little working capital or missing a bond coupon payment and being hauled into bankruptcy court.
Quick ratio =
𝐶𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 + 𝑚𝑎𝑟𝑘𝑒𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑠
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
Current ratio formula =
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡
𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
3.2 Operating Efficiency (EBIT MARGIN)
The metric used to measure a financial operating efficiency is the Operating margin. It is recovered by deducting from company operating profit margin, the variable costs of company products, services, production and marketing. It provides therefore an indication of company cost control management capacity.
15
Operating Margin (EBIT) = 𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑒
= 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 – (𝐶𝑂𝐺𝑆 + 𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠 + 𝐷𝑒𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐴𝑚𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛)
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑒𝑣𝑛𝑢𝑒
COGS: Cost of Goods Sold.
A negative cashflow from operation could indicate that bills are in anticipation on customer invoices payment.
A good cost control management company capacity is crucial for its long-term sustainability. A bad management of this specific aspect can lead to business collapse.
3.3 Profitability
For a company to survive on the long term, a company must reach and maintain profitability. The best metric for evaluating profitability is called Net margin which represents the ratio of profits to total revenues. A larger net margin, especially as compared to industry peers, means a greater margin of financial safety and a better financial position in committing capital into growth and expansion. Especially profit margin means a lot to startup companies. A high profit margin could indicate that a company can survive an economic downturn or other financial setback and still remains in business.
Net margin = 100
× (1 −
𝐶𝑂𝐺𝑆 + 𝑂𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠 + 𝑂𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟 𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠 + 𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡16
3.4 Solvency
Solvency is very related to liquidity. It represents a company ability to meet, not only on short term, its debt obligation on an ongoing basis. In order to be considered solvent, the value of an entity assets must result greater than the sum of its debt obligations. Solvency ratios (interest coverage ratio and debt to assets ratio) measure the company long term debt in relation to its assets or equity. One important metric among the solvency ratios is the debt to equity ratio(D/E). It is a robust indicator of a company long term sustainability, in the sense in which it provides a measurement of debt against stockholder’s equity. It is in consequence, a measurement of investor’s interest and confidence in a company.
A company lower Debt equity ratio indicate that more of operations are being financed by shareholders rather than by creditors. Being financed by shareholders instead of creditors has a great advantage, because shareholders does not charge interest on financing that they are providing to the company. A decreasing trend over time of the D/E ratio is a good indicator of an increasing company financial solidity. However, a correct balance mix should be used between equity and debt financing. A debt ratio greater that 100 %, shows that the company has more debt than assets. A higher leverage debt equity ratio tends to indicate a company with higher risk to shareholder.
Interest coverage ratio = 𝐸𝐵𝐼𝑇
𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑒
Debt equity ratio (D/E) = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
17
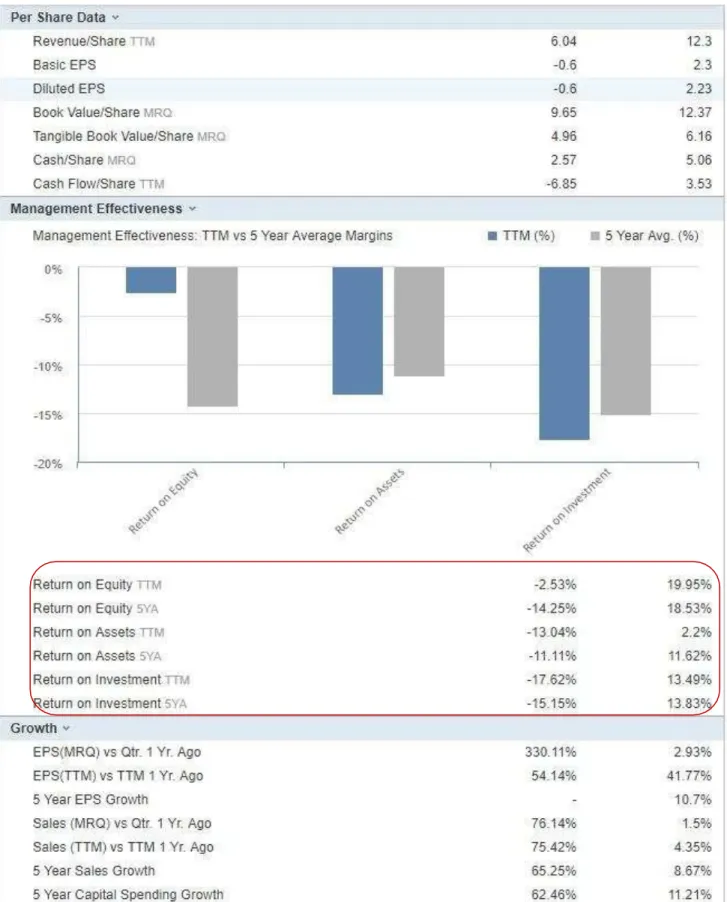
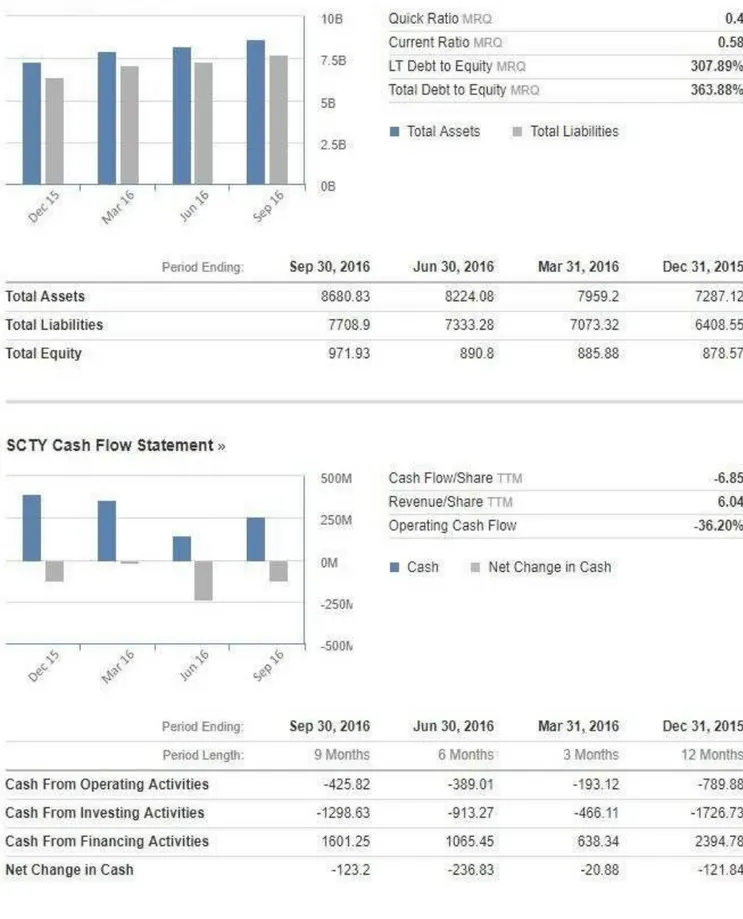
3.5 Analysis of Solar city financial situation
The following images taken from the website www.investing.com provides a financial summary of Solar city at the end of 2015.
18
19
Fig4. Solar City Strength and efficiency
Fig3. Solar city cash flow statement
20
21
22
23
Fig.8. Solar city Balance sheet
24
Diagram 1: Solar City Indicator Hierarchy.
acquisition Debt ratio equity: 2015 0.58 2015: -158.44% 0.4 -126.89% -158,65%
25
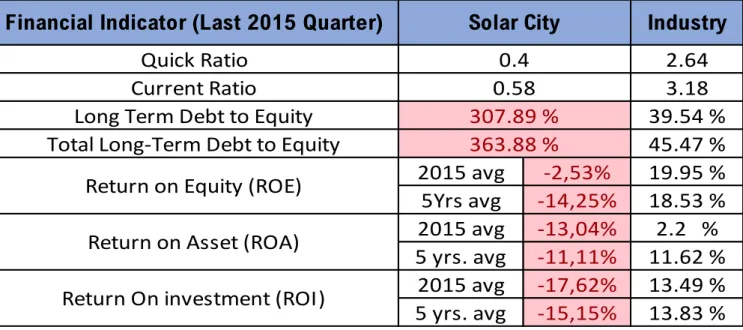
Table 2. Solar City Corp Financial Indicator
Quick Ratio 2.64
Current Ratio 3.18
Long Term Debt to Equity 39.54 %
Total Long-Term Debt to Equity 45.47 %
2015 avg -2,53% 19.95 % 5Yrs avg -14,25% 18.53 % 2015 avg -13,04% 2.2 % 5 yrs. avg -11,11% 11.62 % 2015 avg -17,62% 13.49 % 5 yrs. avg -15,15% 13.83 % Return on Asset (ROA)
Return On investment (ROI)
Financial Indicator (Last 2015 Quarter) Industry
0.4 0.58
307.89 % 363.88 %
Return on Equity (ROE)
26
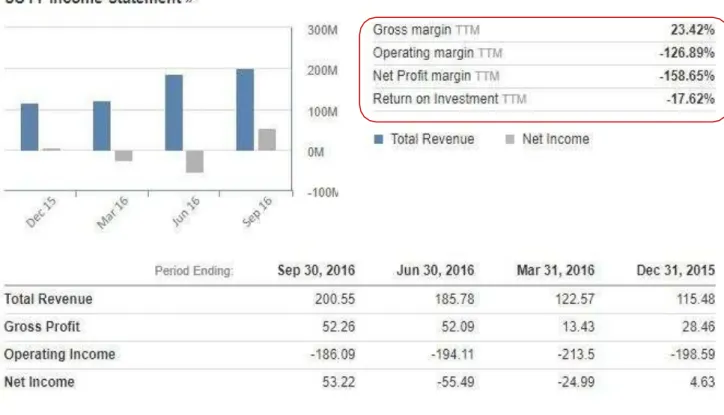
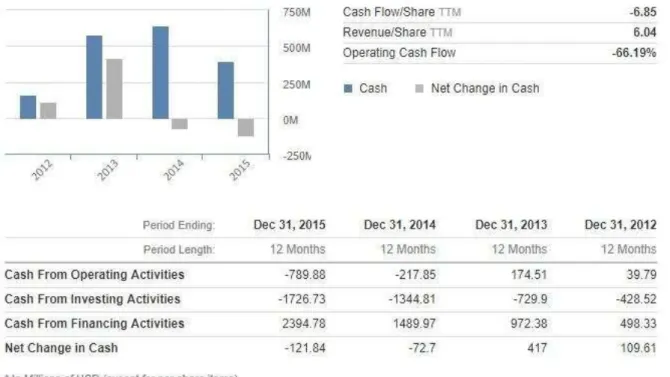
Based on the analysis of the company, Solar city results to present a difficulty in sustainability. First, all the returns ratios of the company are negatives, and under the industry standards. The second relevant observation is that the last 2015 quarter quick ration of the company is 0.4, under 1. From this it is clearly deductible that the company is missing liquidity, therefore uncapable to sustain financially its activities. The last observation concerns the long-term debt to equity of the company, which amounts to 307.89% as shown on table 2. This is alarming because the average long-term debt in the industry is 39.54%. This means that Solar city has approximatively 9 times more long-term debt than other companies in the Solar energy industry. The conclusion is simply that Solar city appears to be highly insolvent. In December 2015, the cash resulting from operating activities is highly negative (-789.89 million of dollars USD), the percentage of the operating cashflow is -66.19%, and the operating margin (EBIT) is - 126.89%. The company is not so well performing from operation efficiency point of view. A quick view on the net profit margin shows a negative value ( -158.65%), the company is also not well profitable.
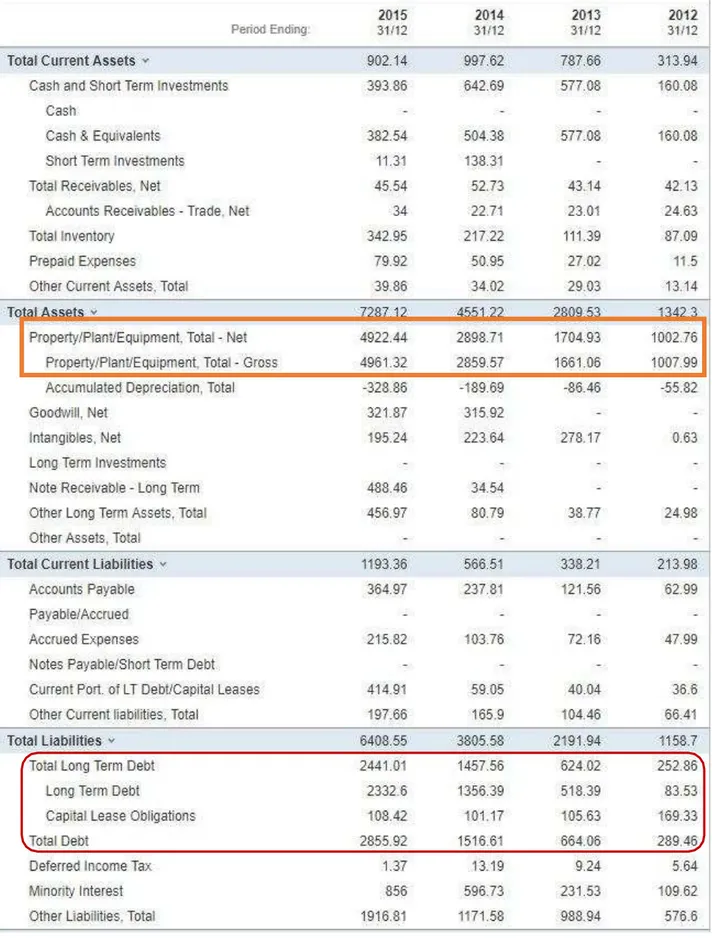
The analysis of the financial health of Solar City, reveals a company facing profitability, solvency, liquidity and operation efficiency, issues. Therefore, SolarCity is having difficulty on being financially sustainable. Despite, all those poor negative performances, The company possess a 4922 million dollars of net tangible asset value, as property, solar power plants, equipment and 2 equity funds for a total of 585 million dollars. The total equity of the company in the end of 2015 among to 878.5 million dollars and the cash from financing activities to 2385 million dollars.
Somehow, in 2016, Tesla Motors announced a conglomerate merging acquisition with Solar City CORP, resulting in a full sustainable vertical integration of both companies with multiple benefits.
27
Chapter 4: Vertical Integration as a Sustainability Mechanism
4.1 Definition of Vertical integration.
Integration among business can be subdivided into 2 categories. It can be distinguished vertical and horizontal integration. During the topic development, it will be the case to discuss only about vertical integration. Vertical integration can be divided also into 3 categories:
• Backwards integration: A business joins another business in the same sector but at an earlier stage of production; When a secondary sector buys a tertiary sector; Or when a primary sector buys a secondary sector. The goal is to guarantee a source of raw materials, components or goods. Another benefit of backward integration is its capacity to increase profit.
• Forward integration: A business buys another business at a later stage of production. This operation guarantee outlet for products, by getting closer to the customer; It therefore provides the benefit of supplying customers absorbing the profits.
• Conglomeration integration: A business buys or merges with another business in a separate unrelated field. Conglomeration integration is done for 2 reasons. First to spread risks, and management ideas, and finally for cross subsidization.
According to Cambridge dictionary, cross-subsidization is a situation in which profits from one activity are used to pay for another activity that is losing money or making less
28
money. The business dictionary defines conglomerate integration as a process whereby a business acquires a substantial number of other unrelated businesses in order to form a large and highly diversified corporation. According to Investopedia, there are two typologies of conglomerates mergers, a pure and a mixed. A pure conglomeration merger is the situation in which the merging firms have completely anything in common. A mixed conglomerate merger is at contrary the situation in which the merger firms are trying also to expand their product lines or target market.
There are many benefits from conglomerate merges which are the increase of market share, synergy, and cross selling opportunities. Firms also merge to reduce losses through diversification.
29
4.2 Solar city Corp ‘s acquisition by Tesla Motors: Vertical
integration as sustainability mechanism
.In 2016, Tesla Motors acquired Solar City Corp, thus this changing the name of the company to Tesla INC. Despite, the economic situation of Solar City Corp, the CEO Elon Musk has decided somehow to vertically integrate its activities with his cousins’ company Solar City Corp as explained in his master plan. More specifically this conglomerate vertical integration would bring value both for Tesla and SolarCity.
According to the FORM 425, filled on the 25/10/2016, the acquisition of Solar City by Tesla not only bears strategic considerations, but also technological and financial benefits. The vertical integration would generate consistent advantages.
Tesla Motors disposes of approximatively 1 billion of available committed sources of liquidity for working capital purpose, plus 300 million of retail lease financing for new costumers. This represents a strong liquidity position. The cost and revenues synergies approach will help SolarCity to reach cash-flow breakeven.
Solar City Corp disposes of 2 equities funds for residential home photovoltaic projects. The first fund has been created with the collaboration of Soros Fund Management and the affiliation of the Quantum Strategic Partners, raising 305 million dollars in cash equities. The second fund has been with the collaboration of Google Partners, consisting of 280 million dollars fund. Solar City Equity is expected to solve Tesla Motors bankruptcy’s risk issue.
The deal is expected to bring to Tesla INC, 150 million of direct synergies costs, optimizing capital expenditures. The vertical integration will also increase potential cost savings
30
through the reduction of, hardware, total ownership, installation and services, costs.
Not only this conglomerate merge will help both compagnies financially, it will also help leverage their core competencies. Tesla Motors competences in design manufacturing and engineering will help to develop solar panel technology making them more aesthetical appealing.
According to the Elsevier journal article on renewable energy, visual appeal has a great
influence on consumer preference for residentials solar panels. The article continues with “Among all visual attributes considered, the shape and pattern of solar cells, and especially panel color, strongly influence consumers evaluation of solar panels visual appeal…. However, when considered within the context of use, panels with colors that match the color of roof are more preferred”.
The Business insider journal stated that “Solar and storage are at their best when they are combined. As one company, Tesla (storage) and Solar city (solar) can create fully integrated residential, commercial and grid-scale products that improve the way energy is generated, stored and consumed.”
All these combinations will generate a single integrated combination consisting in:
• A sustainable energy generation through a solar panel at affordable lower price.
• The ability to store the sun energy source with the help of batteries system such as Powerwall, allowing the use of energy during the night (which was a limitation of Solar city systems).
31
Basically, it will be possible in one single financing (loan agreement) to have an electric vehicle, a solar production system (integrated or not) and storage system.
According to the renewable and Sustainable Energy reviews 94 of 2018 entitled
Interaction between electric mobility and photovoltaic generation: “Electrics Vehicles (EV) could use photovoltaics energy (PV) and benefit from cheap carbon-free electricity for charging. In return, PV systems could use the bi-directional flexibility of EV batteries to maximize their self-consumption. As these synergies operate, economic spillovers from these technologies are expected to improve, thus further leveraging their joint deployment.”
Coupling Electrics vehicles with solar panel energy generation can consistently reduce also the environmental pollution impact as explained in the Apply energy article number 165 entitled Integrating building and transportation energy use to design a comprehensive greenhouse gas mitigation strategy: ” The mitigation strategy including EV’s powered by solar energy obtained from gird-tied solar panels have led to 12.2% CO2 reductions per day … , and the strategy incorporating EVs with off grid source of power was the most successful strategy and resulted in an average 12.38 lbs. /day saving of CO2 emissions.”
32
Chapter 5: Impact of sustainability business on Built
environment
In 2017, Tesla Inc unveils a new product born from synergies acquisition of Solar City Corp and partnership with Panasonics. The new product is the solar roof, which is manufactured in Tesla giga factory, in Buffalo New York.
5.1 Tesla Solar roof Analysis.
From Tesla patent’s number US2018/012973 A1, from May 3, 2018. It is possible to observe constitution of the section of the new material.
33
N° Layer Material constitution
310 Textured
Glass (1900)
Amorphous Silica Low iron Transparent material(optional) 308 Front sheet (top encapsulant) (1904) Polymer
306
Silicon Wafer (Photovoltaic Material) (1906) 304 Bottom encapsulant Layer
Back sheet (1908)
Coated
(depending on the model)
Dielectric module
1704D,1704C, 1704B,1704A Metallic layer 1706C,1706B,1706A
Substrate Coat (Depending) TiO2(100nm) 2400 Al(4nm) 2402 Tio2(5nm) 2404 1702 312 Junction box
Table n.3 Tesla Roof Constitution
Tesla roof tile are divided into 4 categories according to their aesthetics forms:
• The Tuscan Glass Tile • The Slate glass tile • The textured glass tile • The smooth glass tile
34
Table n.4: Tesla roof technical properties.
Tesla Roof Characterisitcs Class Certification
Wind resistance F ASTM D3161
Hail resistance 4 ANSI FM 4473
Fire resistance A UL 790
Compatible with freezing and cold winter Glass standards certifications: ASTM 11379, EN 1096
35
The November 2011 technical report of the National Laboratory of United Stated department of Energy (NREL), gives major information about the analysis of installed rooftop systems in the residential sector. According to the report the photovoltaic roof installation typologies can be summarized as shown on the following figure.
Fig11. Roof PV panels installation Systems typologies.
According to the Tesla Solar roof Marketing plan realized by students from Portland state University, a comparison between different solar roof systems revealed the following table.
36 Tesla
roof Tile
Ceramic Roof tile + Solar system Stone Roof Tile+ Solar system Metal Sheet (stone coated) +Solar system Asphalt shingle +Solar system
Hail rate Best Average Average Best Average
Fire rate Best Best Best Best Low
Wind rate Best Average Best Best Low
Freezing/ cold
weather Good Low Best Good Low
Aesthetic Best Medium Medium Medium Low
37
5.2 From Building Applied Photovoltaics (BAPV) to Building Integrated
Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Wikipedia defines the term Building-Applied Photovoltaics (BAPV), as photovoltaics that are a retrofit – integrated into the building after construction is complete., in other words, it can be defined also as the additive installation of a photovoltaic system, to an already finished envelope.
The first use of PV, as smart grid for decentralize energy harvesting, was born from the initiative “Megawatt” of the Swiss engineer Markus Real in 1986.The initiative consist in the adoption of PV panels systems installation on 333 residentials house in Zurich.
This solution for building encountered a fundamental problem, the aesthetic appealing, raising therefore the possibility of the integration of photovoltaics elements into the building.
The term Building-Integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), are defined as photovoltaics materials that are used to replace conventional buildings materials in parts of the building envelope such as the roof, skylights, or facades.
As explained in the article from Patrick Heinstein, Christophe Ballif and Laure- Emmanuelle Perret- Aebi, Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Review, Potentials, Barriers and Myths. In 1990, first buildings were erected under the PV integration perspective. The first building element completely PV integrated was the semi-transparent, multifunctional, façade of the Public Utilities Building (Stadtwerke), in Aachen (Germany), in 1991. The Energiepark West in Satteins (Austria) was also designed, with a solar façade.
38
The adoption of photovoltaics panels or elements in the built environment provides the advantage of energy generation. Practically the building is moving from energy consumer to energy producer. Integrated photovoltaics have also major benefits over non-integrated elements. First, BIPV presents more economical values, because the initial cost is offsetable, by reducing the capital spent, on both labor and equipment, installations costs, that are required on non-integrated systems, Improving consequently rental and sales returns. Secondly, they provide a more aesthetic attractiveness of the building, therefore mostly easily adoptable by customers. Third they also contribute in daylighting, noise control and overall thermal performance of the building.
Table n6. BIPV products typologies (Source Wikipedia)
BIPV product typologies Characteristics Application Ground Based Rooftop Power plant Hollow color
Light color Red color Blue color Yellow color
Double glass solar panels Square cells
integrated N/A
N/A
Glass Curtain wall
Transparent Skylight
Flexible modules Flats roofs Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CGIS) thin film cells
Amorphous crystalline silicon thin film Crystalline Silicon solar panel
39
Table n.7: BIPV morphologies
Based on the EDG 68 MS article of July 2011, on Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
from the authors Mark Snow and Deo Prasad, there are several factors to consider in the design process of a BIPV such as:
• Electrical efficiency • Availability • Lead time BIPV POSITIONING MORPHOLOGIES ELEMENTS DESIGN Monted on weatherproof Skin Mounted on watertight foil Mounted on extruded polystyrene insulation Integration on
canopies and exterior shading systems
ROOF
FLAT
Amorphous thin + flexible polymer module Copper indium Gallinium
Selenide(CIGS)
PITCHED
ceramic roof tiles+integrated solar modules
solar shingles+flexible thin film cell
free standing flexible module/CGIS seal
FACADES
Transparent and translucent photovoltaics (tin oxide coating) + cell titanium oxide
+ dye coat
N/A
40 • Capital cost
• Energy payback time (EPBT)
• Environmental implications
• Physical characteristics such as color, size, translucency, reflectivity and module compatibility.
A correct architecturally BIPV should present the following characteristics criterium:
• Naturally integrated • Aesthetically pleasing • Well composed • Grid harmony • Well contextualized • Well-engineered
• Innovative new design
PV can be considered also an asset that can add a premium on building property value as explained in the Berkeley National Laboratory publication (second version) of December 2013 “Our analysis offers clear support that a premium exists in the marketplace: Thus; PV systems have value and their contribution to home values must be assessed. We find that premiums in California are strongly correlated with PV system size and weakly correlated with PV systems age, in other words larger systems garner larger premiums and older systems garner smaller premiums.”
41
Chapter 6: Financial application of BIPV: SOLAR REITs.
6.A: Solar Project financing Scheme
6.1. Special Purpose Vehicle Financing model
42
The above figure gives a typical scheme of a Solar Project financing structure, in which many actors are involved with each a specific role to play. Such actors might be divided into three categories:
• Finance companies
• Project management and execution companies • Commercialization companies.
6.1.1 Project funding
6.1.1.1 Equity Sponsor.
The equity sponsor is the Owner of the Photovoltaic plant. The role of the equity sponsor is to buy the shares of the Project Company (Special Purpose Vehicle) through a Shares Purchase Agreement contract. They are also in charge of fixing the global price of the project, by maximizing the return on investment (ROI) and the internal rate of return (IRR) depending on the risk of the project. The equity sponsor is also responsible of funding around 20% of the equity for the PV plant. And finally, the equity sponsor benefit from the Asset and Liability guarantee to secure the reliability of the asset acquired.
43
6.1.1.2 Banks
The Bank is the lender of the PV plant. The banks involved in the PV solar project might be private banks, investment funds, publics banks (direct financing or Counter guaranteed Bank). Banks provides 80 % of financing through a Loan agreement Contract. Banks play an important role in the project.
First, by fixing the debt Service Reserve account (DSRA), through a treasury reserve in order to pay back the loan in case of problems, on a calculation duration of 6 months of the debt servicing. Secondly, Banks are in charge of fixing the guarantees, by, a pledge on the shares of the SPV and assets, a mortgage on the land, an assignment of the PPA receivables, and a delegation of the insurance contracts towards Banks. Thirdly, to set-up counter-guarantees (to facilitate the loan agreement).
44
6.1.2 Project execution and management
.
6.1.2.1 EPC (Engineering Procurement and Construction)
contractor
The engineering, procurement and construction contractor is the builder of the PV plant through an EPC contract, which might involve subcontracting activities. The Key role of the EPC contract consist in first to define precisely the scope of the works. Secondly to commit a schedule. Third to define the guarantee of the performance ratio (>80%) and the possible penalties associated.
6.1.2.2 Operation and Maintenance Contractor (O&M)
The O&M contractor is the operator of the PV plant. They oversee the supervision of the operations and maintenance on the PV plant, and site. An Operation and maintenance contract consist in the definition of, the performance guarantee (Availability rate), along with associated penalties or bonus, and the scope of the maintenance activities composed by the following categories:
• Preventive maintenance (annual technical inspection) • Curative Maintenance (Spare parts replacement) • Inverters guarantee
45
6.1.3 Commercialization
6.1.3.1 Power Purchase agreement (PPA) company
The Power purchase company is any off taker of the electricity production through a power purchase agreement contract. They are involved in the following activities. First in the definition of the electricity Kilowatt-hour price and its indexation (Feed in Tariff, Private Agreements, Green certificates). Secondly, in the definition of the tenor of the power purchase agreement, which a longer duration positively affects the stability for equity sponsor.
6.1.3.2 Lease agreements company
The lease agreement company is the owner of the land or the rooftop. A lease agreement contract consists in, first, the definition of the rent of the land or the rooftop; secondly, the definition of the leader of the lease agreement. (A longer contract duration of the lease leader positively affects the stability of the equity sponsor). And thirdly, the eventual establishment of a dismantling clause, with a tenant obligation to refurbish the land as initially.
46
6.2 Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, Solar Investment Tax credit is one of the most important federal policy mechanisms to support the deployment of solar energy in the United States of America. The ITC is a 30% tax credit for solar systems on residential and commercial properties. According to the Solar industry data, it helped the annual solar industry grows by 1600% since its implementation. Unfortunately, this measure is ending in 2022, and nothing is not yet sure about its extension or suspension. Yet even, if this financing methodology is a great help for developers , it remains very risky due to its connection with political policies , which are one of the most important barriers in BIPV adoption as explained in the renewable energy article number 126 of 2018 , entitled The adoption of building-integrated photovoltaics: Barriers and facilitators , “ Products specifics , stakeholder-specific and institutional barriers are identified. Central product-specific barriers include high initial costs and high complexity. The main stakeholder – specific barriers are low awareness of BIPV, and the reluctance of many architects to adopt BIPV. Institutional barriers refer to political risks.”
Solar City Corp used the same model as describe in the fig.14 below. Even though the company is not sustainable in economic terms, the company has been making cash from financial activities. The company had recourse to the ITC financing. In fact, the company has created 2 funds, one with City Bank, and another one with Credit Suisse, in order to finance over 347 million dollars in solar projects for homeowners. Solar City has also the ability to monetize customer Power Purchase Agreements (PPA) and leases through project financing.
47 98 % of cashflow from Lease agreement s
48
6.B Solar Project Financing in the residential properties Sector
6.3 Warehouse for Energy Efficiency Loans (WHEEL) program
The ITC is not the only public program dedicated to the financing of Solar projects principally in the residential properties sector. Many programs are implemented in this perspective. One other program implemented is the Warehouse for Energy Efficiency Loans (WHEEL) program. It was Developed by the Energy Programs Consortium and the National Association of the State Energy Officials (NASEO), in partnership with the Pennsylvania Treasurer and Citi Bank. The program is active in Pennsylvania, and under consideration in Kentucky, Virginia, Nevada and Mendelsohn. The main objective of this program is the facilitation of residential energy efficiency loan provision.
Fig.14: WHEEL Solar Asset financing (source: US National renewable energy laboratory: Technical report NREL/TP-6A20-62618 February 2015)
49
6.4 The CT Solar Loan for Homeowners Target.
Alike the WHEEL program, the CEFIA has been developing similar warehouse financing approach. This credit enhancement from the State was about 93 million dollars. The Financing program consist in three different loans typologies:
• The Solar Lease for installers
• The CT Solar Loan for Homeowners • The smart E-loan for banks.
For what concerning the CT Solar Loan for residential Homeowners, it has been implemented in 2014. This new residential financing product has come through the partnership of CEFIA, Sungage Financial (a solar loan originator), and Mosaic (a solar crowdsourcing investment platform). CEFIA, through a Special purpose vehicle a Mezzanine Capital, at the amount of 5 million dollars in order to finance solar photovoltaics residential projects.
The NREL report of February 2015 entitled” Credit Enhancements and Capital Markets to fund Solar Deployment: Leveraging Public Funds to Open Private Sector Investment”
provides majors information about the transaction: “CEFIA will leverage this warehouse facility with debt from Mosaic by lending against the cash flow of the residential loans. To recapitalize the SPV , the loans are polled into 500.000$ tranches and sold to Mosaic at 6% yield and 15 year maturity ( the term of the loans).The capital raised remains in the SPV to leverage against tranches as they come in and to buffer against potential defaults. CEFIA retains a first loss position of 20% subordinated debt and Mosaic receives 80% of loan repayment cash streams.”
50
51
6.C: The potential application of BIPV in the real estate industry:
Solar REITS.
According to Wikipedia, Traditional REIT intended as Real Estate Investment Trust can be defined as a company that owns, and in most cases operates, income-producing real estates. REITS can own many different commercial real estate categories, such as offices, warehouses, hospitals, shopping centers, hotels, timberlands, apartments buildings, data centers, self-storage, Cell towers, energy pipelines, and retails centers. According to Investopedia, REITS provides the opportunity to individual investors to buy shares in commercial real estate portfolios that receive income from a variety of properties. REITS might also be engaged in real estate financing activities.
According to Investopedia, REITS can be subdivided in the following categories:
• Equity REITs: These REITs buys, own and manage income producing real estate from which they generate revenues by rent (Not properties reselling).
• Mortgage REITs: The main activity is to lend money to real estate owners and operators by direct financing (mortgages and loans), and indirect financing (acquisition of mortgage backed securities). They generate revenue principally through the net margin which consist in the spread between the interest earned from mortgages and loans and their funding cost.
• Hybrids REITs: Theirs activities result in a combination of owning properties and mortgage financing.
52
REITs presents a valuable investment, since REITs pay its investors 90% of the annual profits, which are not taxed. There is not a double taxation, because only investors are taxed on their dividends, which makes it more attractive.
The article of Rec Solar Energy insights blog of September 29 th, mentioned that “Seeing the successful real estate development and financing model (referring to traditional REITs), the solar industry wanted to create Solar REITS (Renewable Energy Investment Trusts) that would bundle investors to fund solar projects or solar loans and pay out dividend to individual investors.”
But the creation of such funds, under the traditional REIT scheme is facing some barriers as the technical report NREL/TP-6A20-55396 of June 2012 from the Us National Renewable Energy Laboratory, entitled The Technical Qualifications for Treating Photovoltaics Assets as Real Property by Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):“There are only two types of property according to IRS. Real and personal, and the terms are mutually exclusive. If a solar asset is designated to be personal property, it would be limited to being 25% or less of a REIT’s assets and might limit the percent of income a REIT receives from the solar asset. The following sections will explore the fundamental characteristics of PV systems in relation to the properties of permanence, passivity, and being integrated as a system.”
In order to be then legally adopted, two perspectives are to be considered. First, the adoption of a new political policies recognizing, and allocating a statue to a “Solar REIT”, or a possible upgrade in the definition of a REIT. Presently, nothing yet has been done so far in both directions. Building integrated technologies appears to be a high potential solution for the future legal implementation of Solar REITs, in the incertitude of the renewal issues of the Solar investment tax credit.
53
Chapter 7: Conclusion
In Conclusion, in order to strategically reduce the global CO2 emissivity impact, it is truly important to target the residential sector, which reveals to be a very critical component according to global data. One of the solutions might reside in the adoption of the building PV integrated technologies, as a support in the production and storage of solar energy, especially for homeowners. Yet, the difficulty in financing accessibility, couple to policies risks still represent barriers. Despite all these limitations, some greens businesses are trying to survive through innovative solutions with the help of publics financing collaboration. All these efforts might produce great results in the dissemination of clean and affordable energy for all, by the mean of PV systems acquisition costs reduction, and technological simplification. The new materiality known as the solar roof will represent a key factor for the residential sector. The potential of this technology will have a drastic impact on the way that the built environment consume energy. It’s passive role in the consumption of energy, might know a paradigm shift. The way residential dwellings and even buildings, are designed, built and construct, will probably be affected by this new technology. This is a step ahead in the development of smart buildings, whereas the built environment is becoming, an autonomous, smart, efficient, intelligent, independent, and connected entity. It is undeniable to say that energy generation is now a full integrated fundamental function among all the others of the 21-century building. This new capacity to generate electricity, might play a key indispensable role in the electric mobility (cars, trucks, drones, robots…), by creating more proximity, simplicity and comfort in its use. This new wave might also play a key role in the energy utility consumption sector. New technologies, and new energy consumption behaviors in the residential, medical, and industrial, real estate sectors, might thus arise, gravitating around the ecosystem of clean and
54
cheap energy generated by integrated photovoltaic elements. Developers might have now the opportunity to fully include energy generation in their asset without having to border to much about legislation. This new business opportunity might lead to the creation of new REITS (mortgage or hybrids) typologies, where assets are entirely composed by building integrated photovoltaics elements. Yet many challenges remain. The large-scale development, and deployment of BIPV, as for instance the solar roof, might be conditioned to local realities, such as climatic, economic, geographic, and technological factors. The potentials business benefits of these technologies are so high that it is envisaged to see Tesla INC to breakthrough in the future in the Real Estate Industry as a possible Spin off, or another probable merger.
55
References
• https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainable_business • https://new.usgbc.org/leed https://www.tesla.com/about • https://www.britannica.com/topic/Tesla-Motors • https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tesla,_Inc. • https://mse238blog.stanford.edu/2017/07/shuyuw/teslas-master-plans-for-the-future-part-i- and-ii/• Wikipedia: Building integrated photovoltaics. https://www.seia.org/initiatives/solar-investment-tax-credit-itc
• https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0960148118304087?token=71E1D623408C9EB 1 750782398EBB932B866A405F2AD9490C14EF3632B724B693CF1CE554097809F2052FC E21C99DA140
•
https://www.ourenergypolicy.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/TrackingCleanEnergyProgress2017.pdf (tracking clean energy
report)
•
https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals/goal-7-affordable-and-clean-energy.html
• https://doi.org/10.1142/7204 Fundamentals of Sustainable business, Mattew Tueth
• https://www.tesla.com/blog/secret-tesla-motors-master-plan-just-between-you-and-me (
Tesla Master Plant)
• https://solarthermalmagazine.com/about-solarcity-a-historical-account/
(Solar city)
• https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.07.021 (Understanding the role of visual appeal in
consumer preference for residential solar panels
• https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1364032118304751?via%3Dihub
(Interactions between electric mobility and photovoltaic generation: A review)
• https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306261915014853?via%3Dihub
(Integrating building and transportation energy use to design acomprehensivegreenhouse gas mitigation strategy)
56
• https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2947&context=etm_student
projects (Tesla Solar Roof Marketing Plan)
• https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/85216706.pdf ( Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV):
Review, Potentials, Barriers and Myths )
• Snow, Mark, and Deo Prasad. “Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV).” Environment
Design Guide, 2011, pp. 1–15. JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/26151891. Accessed 18 Mar. 2020.
• https://emp.lbl.gov/sites/all/files/lbnl-6484e.pdf (Exploring California PV Home Premiums)
• https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0960148118304087?via%3Dihub
(The adoption of building-integrated photovoltaics: barriers and facilitators)
• https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy15osti/62618.pdf (Credit Enhancements and Capital Markets
to fund Solar Deployment: Leveraging Public Funds to Open Private Sector Investment)
• https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241910070_Technical_Qualifications_for_Treat
ing_Photovoltaic_Assets_as_Real_Property_by_Real_Estate_Instment_Trusts_REITs
• https://www.worldgbc.org/sites/default/files/UNEP%20188_GABC_en%20%28web%29.pdf
(Global Status Report).
• https://www.divestopedia.com/definition/4778/tangible-asset-value-tav Tangible asset value
57
Figures index
Fig .1 SCTY income Statement………. 17
Fig 2. Solar City Long term debt and assets……… 18
Fig 3. Solar city cash flow statement………. 19
Fig 4. Solar City ratios, current vs industry………. 20
Fig 5. Solar city Corp Management effectiveness………. 21
Fig 6. Solar City Cash Flow Activities………. 22
Fig 7. Solar city Balance sheet………. 23
Fig.8. Solar City Cash Flow Statement……… 24
Fig.9 Tesla Solar Roof tile (From Tesla Patent) ……… 32
Fig.10 Tesla Roof categories (From Tesla website) ………. 33
Fig 11. Roof PV panels installation Systems typologies………. 35
Fig 12. Solar Project Finance shareholders review……… 41
Fig.13: Solar City Tax Equity Financing Partnership Model……… 47
Fig.14: WHEEL Solar Asset financing (source: US National renewable energy ………. 48
laboratory: Technical report NREL/TP-6A20-62618 February 2015) Fig.15: CT Solar Loan structuring………. 50
58
Tables
Table 1. Green Business standards……… 10
Table 2. Solar City Corp Financial Indicator………. 25
Table n.3 Tesla Roof Constitution……… 33
Table n.4: Tesla roof technical properties……… 34
Table 5. Tesla solar roof vs other Solar adaptable solutions………. 36
Table n6. BIPV products typologies (Source Wikipedia) ……… 38