2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Yeast strains and growth media
The panel of 11 Candida glabrata clinical isolates used in this study was selected to represent different levels of fluconazole susceptibility (Table 1) (Sanguinetti et al., 2005; Torelli et al., 2008). C. glabrata isolates were grown in Sabouraud broth at 30°C for 18 hours. All isolates were maintained on Sabouraud agar for the duration of the study.
Table 1: Candida glabrata clinical isolates
C. glabrata isolate Fluconazole susceptibility (MIC µµµµg/ml)
BPY40 4 a Cg1 16 b BPY44 256 a BPY59 64 a BPY150 32 a BPY221 16 a BPY233 256 a BPY269 256 a BPY270 16 a BPY498 128 a BPY597 128 a a
Susceptibility data from Sanguinetti et al., 2005, Torelli et al., 2008;
b
2.2 Antimicrobial peptide and antifungals
Synthetic Hepcidin (Hep-20) was purchased from Peptide Specialty Laboratories GmBH (Heidelberg, Germany). Analysis of the synthetic peptide by reverse-phase high performance chromatography and mass spectrometry revealed purity higher than 98%. Hep-20 was diluted in milli-Q water to obtain a stock solution of 1 mg/ml. Amphotericin B (AmB, suspended in DMSO, Sigma) and fluconazole (dissolved in DMSO, Sigma) were suspended in DMSO into 20 mg/ml and 2.6 mg/ml, respectively. Caspofungin (Merk Sharp and Dohme, USA) was diluted in water solution to a final concentration of 0.64 mg/ml.
2.3 Killing kinetics of Hep-20 in sodium phosphate buffer (SPB)
Fungicidal activity of Hep-20 was evaluated in a microdilution assay performed in 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer (SPB, pH 7.4 and pH 5.0). Yeast isolates were grown in Sabouraud medium to exponential phase at 30◦C and suspended in SPB at a concentration of 1 ×107 cell/ml. Ten microliters of fungal suspension were incubated in the presence of different concentrations of the peptide (50–200 µg/ml) in 100 µl of SPB at pH 7.4 or pH 5.0. Following 90 minute incubation, samples were diluted ten-fold in SPB and 200 µl were plated onto Sabouraud plates and incubated for 24 hours to determine CFU number. Fungicidal effect was defined as a reduction in the number of viable yeast cells ≥ 3 log10 CFU/ml, in comparison to the untreated control (Maisetta et
al., 2010). Killing experiments were repeated using SPB at different pH values, ranging from 7.4 to 5.0 (7.4, 6.6, 5.8 and 5.0), in order to evaluate the effect of pH on Hep-20 antifungal activity. Hep-20 killing kinetics were performed with two representative isolates of C. glabrata, Cg1, dose-dependent susceptible to fluconazole and BPY44, fluconazole resistant (Table 1). Time killing curves were performed in SPB (pH 7.4 and pH 5.0) in the presence of two different concentrations of the peptide (50 and 100 µg/ml at pH 5.0 and 7.4, respectively) and were monitored at different time points: 15, 30, 60, 90 minutes and 24 hours; samples were diluted ten-fold in SPB and 200 µl were plated onto Sabouraud plates and incubated for 24 hours to determine CFU number.
2.4 Evaluation of antifungal activity of Hep-20 in combination with antifungal drugs SPB
The fungicidal activity of Hep-20 in the presence of the antifungal drugs amphotericin B (AmB) and caspofungin was evaluated in killing kinetics performed using sub-fungicidal concentrations of the peptide and antifungals. The assay was performed for each combination in SPB at pH 5.0 and at incubation times varying between 15 minutes and 24 hours at 30◦C. Time kill experiments were performed in a final volume of 100 µl: 10 µl of yeast suspension (1×107 CFU/ml), 10 µl of Hep-20 (25 µg/ml), 10 µl of caspofungin (1 µ g/ml) or AmB (0.5 µ g/ml) and 70 µl of SPB pH 5.0. The mixture was incubated for 90 minutes at 30◦C, and 10-fold dilutions were plated onto Sabouraud agar. The number of CFU/ml was evaluated after 24 hours of incubation at 30◦C. A synergistic effect was defined as a reduction in the number of CFU/ml ≥ 2 Log10,
between a given combination and its most active component.
The activity of the peptide in combination with fluconazole was evaluated by the fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) (Odds, 2003) calculated by the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) checkerboard method for the two representative isolates of C. glabrata. The sub-inhibitory peptide concentrations used were 50 and 25 µg/ml, while fluconazole concentrations were 4, 2, and 1 µg/ml for the dose-dependent susceptible isolate (Cg1) and 64, 32, 16 µg/ml for the resistant isolate BPY44. MIC tests were performed in RPMI 1640 (Trek Diagnostic System, Cleveland, USA) diluted eight-fold in SPB (pH 5.0). FICI was evaluated according to the following formula: (MIC fluconazole in combination/MIC fluconazole alone) + (MIC Hep-20 in combination/MIC Hep-20 alone). The drug interactions were defined as synergistic if FICI value was ≤ 0.5, indifferent (no interaction) with a FICI value ranging from 0.5 to 4, and antagonistic if the FICI was > 4 (Odds, 2003).
2.5 Fungicidal activity of Hep-20 in an artificial vaginal fluid simulant (VFS)
A vaginal fluid simulant resembling human vaginal secretions was used to evaluate whether the activity of Hep-20 was maintained in such condition. The VFS was prepared as described by Owen and Katz and the solution pH adjusted to 4.5 using HCl
(Table 2) (Owen and Katz, 1999). The solution was then filtered through a 0.22 µm filter (MerckMillipore, Rome, Italy) and stored at -20°C.
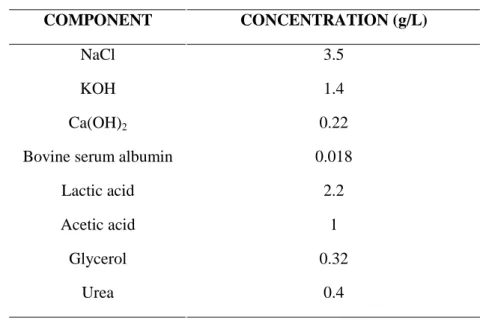
Table 2. Composition of artificial vaginal fluid, pH 4.5
COMPONENT CONCENTRATION (g/L)
NaCl 3.5
KOH 1.4
Ca(OH)2 0.22
Bovine serum albumin 0.018 Lactic acid 2.2 Acetic acid 1
Glycerol 0.32
Urea 0.4
The fungicidal activity of Hep-20 against BPY44 was evaluated in a microdilution assay performed in 4-fold diluited VFS, supplemented with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) a chelator of divalent cations (1 mM final concentration).
C. glabrata BPY44 fluconazole resistant isolate was grown in Sabouraud medium to
exponential phase at 30°C and suspended in deionized-water at a concentration of 1×107cell/ml. Ten microliters of fungal suspension were incubated in the presence of Hep-20 (100 and 200 µg/ml) in 100 µl of VFS with and without 1 mM EDTA. Following incubation, samples were diluted ten-fold in water and 200 µl were plated onto Sabouraud plates and incubated for 24 hours to determine CFU number. The fungicidal effect was defined as a reduction in the number of viable yeast cells ≥ 3 Log10 CFU/ml, in comparison to the untreated control (Maisetta et al., 2010). Time
killing curves were performed on C. glabrata, BPY44, fluconazole resistant in diluited VFS suplemented with 1 mM EDTA, in the presence of 200 µg/ml Hep-20 and were monitored at different time points, from 15 minutes to 24 hours; samples were diluted ten-fold and 200 µl were plated onto Sabouraud plates and incubated for 24 hours to determine CFU number.
2.6 Evaluation of antifungal activity of Hep-20 in combination with antifungal drugs in VFS
The antifungal activity of Hep-20 in VFS alone and in combination with the antifungal drugs amphotericin B (AmB) and caspofungin was evaluated in 4-fold dilution of VFS with EDTA at a final concentration of 1 mM in killing kinetics performed using sub-fungicidal concentrations of the peptide and antifungals. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of fluconazole were used in killing experiments assessing the activity of Hep-20/fluconazole combination. The killing assay was performed for each combination in a final volume of 100 µl: 10 µl of BPY44 yeast suspension (1×107 CFU/ml), 10 µl of Hep-20 (100 µ g/ml) in combination with fluconazole or 10 µl of Hep-20 (50 µg/ml) in combination with caspofungin, 10 µl of fluconazole (128 µ g/ml) or 10 µl of caspofungin (0.1 µ g/ml) or 10 µl amphotericin B (AmB, 1 or 2 µg/ml). The fluconazole/20 mixture was incubated for 20 hours at 30°C, while the Hep-20/capofungin and Hep-20/amphotericin B combinations were incubated for 1.5 hour at 30°C. At end points 10-fold dilutions were performed and 200 ml were plated onto Sabouraud agar to determine CFU number. A synergistic effect was defined as a reduction in the number of CFU/ml ≥ 2 Log10, between a given combination and its
most active component.
2.7 Human vaginal fluid (HVF) extraction
Human vaginal fluid (HVF) was collected by three healthy donors (D1-D3), who ranged in age from 26 to 42 years and had regular menstrual cycles of approximately 28 days. To account for protein content variability over the menstrual cycle, HVF was collected twice per donor (D-1 and D-2) before and after ovulation. The human vaginal fluid was collected as described by Valore and coworkers with minor modifications: tampons (O.B.® Pro ComfortTm MINI) were inserted in vagina for 8-10 hours and then transferred in centrifuge tubes. Thirty ml of 10 mM SPB, pH 5.0, were added to each tampon and incubated with rotation at 37°C. The fluid retained in tampons following a 4 hour incubation was squeezed out in a centrifuge tube with the related washing SPB, by
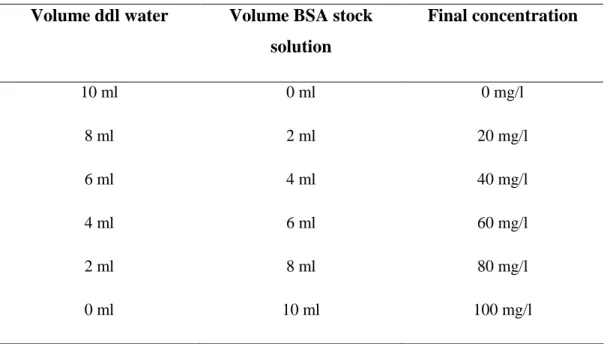
centrifuging at 4800 rpm to remove epithelial cells and tampon debris. In order to reverse the extreme dilution due to the extraction procedure, the fluid was centrifuged trough a 3 KDa filter spin unit (Merck Millipore) for 3-4 hours up to a final volume of 1 ml. The effective protein concentration of HVF was then measured by Lowry assay, versus a Bovine Serum Albumin standard solution (BSA stock solution 100 mg/L) (Lowry et al., 1951). Calibration curve was calculated using BSA stock solutions serially diluted as shown in table 3.
Table 3. Dilution from BSA stock solution
Volume ddl water Volume BSA stock
solution Final concentration 10 ml 0 ml 0 mg/l 8 ml 2 ml 20 mg/l 6 ml 4 ml 40 mg/l 4 ml 6 ml 60 mg/l 2 ml 8 ml 80 mg/l 0 ml 10 ml 100 mg/l
The samples, negative control and BSA standard solutions were appropriately diluted and 500 µl of each sample were added to a 10 ml glass tube. Seven hundred microliters of Lowry solution were added to each sample and all tubes were incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature in the dark. One hundred microliters of light-sensitive Folin reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy) (5 ml Folin Ciocalteu’s Phenol Reagent + 6 ml ddl water) were added to each sample. The mixture was incubated for 30 minutes in the dark at room temperature. The amount of proteins in the sample was estimated by reading the absorbance at 750 nm of the end product of the Folin reaction against a standard curve. Human vaginal fluid was diluted appropriately and stored at -20°C for further investigations.
2.8 Fungicidal activity of Hep-20 in HVF
The human vaginal fluid was collected and quantified as described above. The fungicidal activity of Hep-20 against BPY44 was evaluated by killing assay performed in HVF at two different protein contents: 2 g/l and 0.018 g/l in order to considered biological variability of HVF (Tomás and Nader-Macías, 2007). C. glabrata BPY44 was grown in Sabouraud medium to exponential phase at 30°C and suspended in dd-water at a concentration of 1×107cell/ml. Fungal suspensions were incubated in the presence of Hep-20 (ranging from 6.25 to 100 µg/ml) in a final volume of 100 µl of HVF with and without 1.5 mM EDTA. Following incubation for 15 minutes to 24 hours at 37°C, each mixture was diluted ten-fold in water and 200 µl were plated onto Sabouraud plates and incubated for 24 hours to determine CFU number. The fungicidal effect was defined as a reduction in the number of viable yeast cells ≥ 3 Log10 CFU/ml,
in comparison to the untreated control (Maisetta et al., 2010).
2.9 Haemolytic assay
The hemolytic activity of the peptide was evaluated by determining the amount of the released hemoglobin from a 4% suspension of fresh human red blood cells (RBCs) in 10% citrate phosphate dextrose at OD450. Human RBCs were harvested by centrifuging
at 1000 × g for 10 min at 4°C and suspended in an equal volume of phosphate buffered saline (PBS). RBCs were washed three times in PBS. RBCs (100 µl) were diluted to 8% (v/v) in PBS, transferred to a 96-well microtiter plate and mixed with 100 µl of Hep-20 solution at the desired concentration. The Hep-20 concentrations tested ranged from 6.25 to 200 µg/ml. The assay was performed in triplicate for all the combinations included. Cells incubated with 100 µl of PBS alone served as a negative control, while RBCs incubated with 100 µl of either 0.2% Triton-X or 2% Tween were used as positive controls (100% lysis). The microtiter plate was incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes and centrifuged at 1000 × g for 20 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant (100 µl) was then transferred to a new plate and the OD450 was measured with a microtiter plate
calculated according to the following formula: [(OD450 in the peptide suspension
−OD450 negative control in PBS)/(OD450 of positive control − OD450 negative control in
PBS)] × 100.
2.10 Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) isolation and A549 culturing
Blood obtained from healthy volunteers was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 10% (vol/vol) sodium citrate and layered on a standard density gradient (Lympholyte®-H, Cedarlane®, Euroclone, Milan, Italy). Following centrifugation at 160 × g for 20 minutes at room temperature, supernatant was removed, without disturbing the lymphocyte/monocyte layer at the interface, in order to eliminate platelets. The gradient was further centrifuged at 800 × g for 20 minutes, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were collected from the interface. Cells were washed three times with PBS containing 0.1% (wt/vol) bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma-Aldrich) and 10% sodium citrate (Sigma-Sigma-Aldrich), and resuspended in RPMI 1640 (Euroclone) supplemented with 4 mM L-glutamine and 20% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS, Euroclone) at a final cell concentration of 1x106 cells/ml.
Human non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells (ATCC® Number CCL-185™, LGC Standards, Sesto San Giovanni, Italy) were cultured in tissue culture flasks in D-MEM (Euroclone) supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine and 10% heat-inactivated FCS. Cell cultures were maintained in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. When cells grew
to confluence, they were treated with Trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich) and split in new flasks.
2.11 Propidium iodide staining of PBMCs and A549 cell line incubated with Hep-20
Cell viability was analysed in flow by cytometry evaluating propidium iodide (PI) incorporation by PBMC and A549 cells after a 24 hour exposure to Hep-20. Propidium iodide is a membrane impermeant fluorescent dye that is normally excluded from viable
cells; once it is internalized by dead cells, it binds to nucleic acids, resulting in cell staining. PBMCs were isolated as described above; 100 µl from the cell culture were seeded in a 96-well microtiter plate (1x105 cells/well) and mixed with an equal volume of RPMI-1640 containing Hep-20 at desired concentrations (12.5-200 µg/ml final concentrations). Cells incubated with complete medium alone served as negative control, while PBMCs incubated with cycloheximide (Sigma-Aldrich) (2 mg/ml final concentration) were used as positive control. Plates were incubated in a 5% CO2
atmosphere at 37°C for 24 hours. Cells were then transferred into 12 x 75 mm culture tubes and washed in D-PBS. Five microliters of a 50 mg/L solution of PI (Sigma-Aldrich) were added to each tube. Tubes were then incubated for 4 minutes in the dark. Following staining, 15 000 events were acquired ungated in a FACSort flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Samples were analysed using CellQuest software (BD Biosciences). In order to evaluate PI incorporation by A549, cells were detached with trypsin from culture flasks and diluted in D-MEM supplemented with 10% FCS and 2 mM L-glutamine (5x104 cells/ml final concentration). Two hundred microliter from the suspension were seeded in a 96-well microtiter plate (1x104 cells/well), and cells cultured in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C for 24 hours to allow
adhesion. Fifty microliter of complete medium containing Hep-20 at desired concentrations or cycloheximide were then added to each well. Following a further 24 hour incubation, cells were harvested by trypsinization and transferred into culture tubes, exposed to PI and analysed as described for PBMCs.
2.12 XTT reduction assay on PBMCs and A549 cell line incubated with Hep-20
Hep-20 effect on cell viability was also assessed using a colorimetric assay based on the reduction of the 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide tetrazolium salt (XTT) into a water soluble orange formazan product by mitochondrial dehydrogenases of viable cells. The XTT-PMS solution was prepared according to Scudiero and colleagues (Scudiero, et al., 1988). In order to improve cellular reduction of XTT, N-methylphenazonium methyl sulphate (PMS), an electron coupling agent, was used. Briefly, XTT (Sigma-Aldrich) was prepared at 1 mg/ml in prewarmed (37°C) D-PBS and PMS at 5 mM in D-PBS (1.53 mg/ml) (Sigma-Aldrich).
A 0.025 mM PMS-XTT solution was prepared mixing 5 ml of fresh XTT (1 mg/ml) and 25 µl of 5 mM PMS immediately before use, and sterilized by filtration (0.22 mm, Millipore). PBMCs and A549 cells were suspended in complete medium and seeded in a 96-well microtiter plate as described above. Cells were then incubated with Hep-20 at desired concentrations (12.5-200 µg/ml final concentrations), complete medium alone as negative control and triton-X 100 (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy) (0.5% v/v final concentration) as positive control. After a 24 hour incubation in presence of 5% CO2, 50 µl of the XTT-PMS solution were added to each well. Following a further incubation (3 hours and 1 hour for PBMCs and A549, respectively) the optical density (OD450 nm)
was measured using a microplate reader (Model 550, BIO-RAD, Milan, Italy), in order to quantify the formazan, production, which gave an indirect measure of cell viability.
2.13 Evaluation of Hep-20 degradation in HVF
Hep-20 was incubated with HVF (protein content 2g/l) from D1-D2 in agitation for 90 minutes and 24 hours at 37°C. Four-fold diluted HVF with and without of 1.5 mM EDTA, and without peptide were analysed to exclude the presence of the Hep-20 in the fluid. Hep-20 (5 µg) incubated alone was used as negative degradation control. HVF appropriately diluted was incubated with Hep-20 (5 µg) in the presence and absence of EDTA. Following incubation of 90 minutes and 24 hours, samples and controls were boiled for 10 minutes in SDS-loading buffer (50 mM TrisCl pH 6.8, 100 mM dithiothreitol, 2% SDS, 0.1% bromophenol blue and 10% glycerol) and separated on a 17.5% Tricine/SDS-PAGE (Schägger and Von Jagow, 1987). Molecular weight marker (7-175 kDa) and samples were processed for 2 hours in stacking gel (4 % polyacrylamide, Sigma-Aldrich) at 10 mA and 4 hours at 30 mA in separating gel. Following electrophoresis gels were stained over night with EZ blue reagent (Sigma Aldrich) and bands visualised with the Image Master apparatus (VDS, Ge Health Care, Milan, Italy).
2.14 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Instat software (GraphPad, USA). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) 2 × 2 factorial experimental design was used to analyze synergism of Hep-20 and amphotericin B in SPB pH 5.0. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. One-way ANOVA was used to evaluate the activity of Hep-20 and synergic effect on Hep-20/caspofungin and Hep-20/fluconazole in VFS. One-way ANOVA was also performed to evaluate the activity of Hep-20 in HVF and for cytotoxicity studies. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.